X-rays, UV rays, and IR rays have found many applications in our daily lives. These are dominating the technology world and are used in the working of many instruments.
The medical and research field has seen tremendous usage of these waves. Ultrasound waves have also been widely used in medical technology and the case of research.
These also harm humans, but given the proper use of the waves, they can be beneficial in certain aspects.
The far-fledged reach of technology and its development have made use of electromagnetic waves and sound waves in several ways to help ease the difficulties of humans.
The energy of these waves can be used in various methods or can be converted to some other type of energy for use.
Key Takeaways
- X-rays are electromagnetic radiation, while ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves.
- X-rays can penetrate dense tissues and create images of bones, while ultrasound can create images of soft tissues and organs.
- X-rays are used to diagnose broken bones or dental issues, while ultrasound is used for pregnancy monitoring and detecting organ abnormalities.
X-Ray vs Ultrasound
An X-ray is a type of electromagnetic radiation that can penetrate through solid objects, such as the human body, and can help diagnose fractures. Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to produce images of internal organs and tissues, is noninvasive, and does not involve any radiation exposure.

X-rays are electromagnetic waves having wavelengths ranging from 0.01 nm to 10 nm. These are transverse waves having a frequency ranging from 1016 Hz to 1020 Hz.
X-rays have the power to ionize atoms and are used in the treatment of cancer.
Ultrasound waves are sound waves that have a frequency higher than that of 20 kHz. These sound waves are longitudinal in nature and are not audible to the human ear as the human hearing range is 20 Hz- 20 kHz.
These longitudinal sound waves require a traveling medium for their propagation.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | X-ray | Ultrasound |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Electromagnetic waves having a wavelength of 0.01 nm- 10 nm. | Sound waves having a frequency greater than 20 kHz. |
| Frequency | 1016 Hz – 1020 Hz | Greater than 20 kHz |
| Nature of waves | Transverse waves | Longitudinal waves |
| Ionizing capacity | Can ionize atoms and molecules and also penetrates human tissues. | Cannot ionize the atoms and molecules. |
| Risks | Found to carry the risk of cancer. | Possess no risks. |
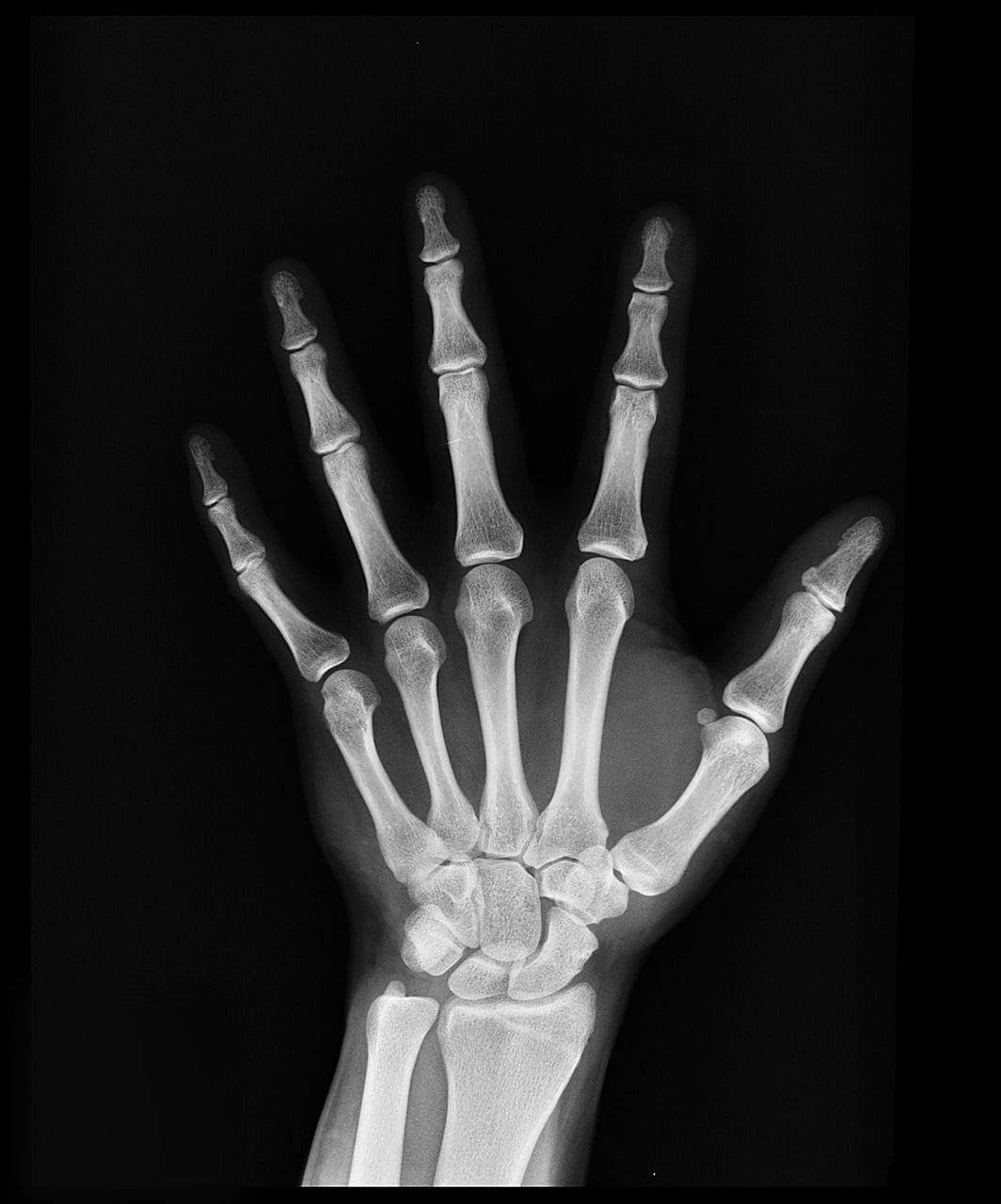
What is X-ray?
X-rays were discovered by Wilhelm Rontgen. These are electromagnetic waves with a very high frequency, the frequency range being 1016 Hz – 1020 Hz.
The X-rays photon consists of some energy which can be calculated by the formula E= hf (where f is the frequency of photon and h is Plank constantly).
The energy of X-rays ranges from 100 eV – 100 keV. X-rays can be divided into two categories based on their energy: hard X-rays and soft X-rays.
X-rays whose photon energy is above 5 keV are hard X-rays. X-ray photons having energy less than 5 keV are known as soft X-rays.
Hard X-rays have better penetration capability than soft X-rays.
Due to the penetration capability of the x-rays, they are now used in radiography. These electromagnetic waves can easily penetrate human tissue and hence find use in medical purposes.
The most common field employing this is in the treatment of cancer. X-rays have a shorter wavelength compared to other electromagnetic waves, which helps in achieving higher resolution.
This is made of used in the technique called X-ray crystallography.
X-rays have very high energy, and due to the capability of ionization of atoms and molecules, they can also be a carcinogen.
Applications of X-rays: X-ray crystallography, Mammography, CT scan, Airport security system to check bone fractures, analyzing and checking of paintings, microscopy, and quantitative analysis.
What is Ultrasound?
The normal human hearing range is 20 Hz – 20 kHz. This is called the audible range, while the sounds above this limit are known as ultrasound.
Ultrasound waves are sound waves that have a frequency range above 20 kHz. They are mechanical acoustic waves and require a traveling medium.
The human ear cannot detect these sounds, but some animals, such as dolphins and bats, can hear these sounds and also produce them. They use this sound for navigation in pitch-dark areas.
Ultrasound has many applications in the medical field, military, communication, navigation in seas, research, and other areas.
One of the most widely used ultrasound technology is Ultrasonography, which is a diagnostic technique. The equipment uses Doppler shift and the retiring time of the echoed sound waves for diagnosis purposes.
Usually, piezoelectric crystals are employed for the production of ultrasound. This crystal deforms when an electric potential is applied, the effect being known as the piezoelectric effect.
The deformation directly depends upon the amount of potential applied. Some of the applications of ultrasound are ultrasonic cleaning, crack detection, echocardiography, lithotripsy, ultrasonography, echolocation, and SONAR (Sound Navigation and Ranging technique).

Main Differences Between X-ray and Ultrasound
- X-rays are electromagnetic waves, while ultrasound wave is categorized as a mechanical acoustic wave.
- The frequency range of X-rays is 1016 Hz – 1020 Hz, while the frequency range for ultrasound waves is above 20 kHz.
- X-rays can ionize atoms and molecules, while ultrasound cannot.
- X-rays have tissue penetration capability, while ultrasound cannot.
- X-rays are high energy and can cause damage to the human body, while ultrasound is safe to use.
- X-ray is found to cause cancer and is a carcinogen, whereas ultrasound does not cause cancer.

The detailed comparison and technical details of X-rays and ultrasound waves, along with their respective risks and applications, provide valuable insights for professionals, scholars, and individuals interested in understanding these sophisticated technologies.
The detailed scientific information and comparative analysis of X-rays and ultrasound waves contribute to a deeper understanding of their potential benefits and risks, guiding us in utilizing these technologies responsibly and effectively.
Absolutely, the comprehensive explanations and practical examples elucidate the complexities and nuances of X-rays and ultrasound waves, enhancing our knowledge of their role in modern science and medicine.
The applications of X-rays in radiography, cancer treatment, and other fields, along with ultrasound waves in ultrasonography and diagnostic techniques, demonstrate the diverse and beneficial uses of electromagnetic and sound waves in modern technology and medicine.
Absolutely, the practical applications and uses of X-rays and ultrasound waves underscore their indispensable roles in advancing medical diagnostics, treatments, and scientific research for the benefit of humanity.
The comprehensive information and comparisons of X-rays and ultrasound waves, accompanied by their historical context and practical applications, provide valuable knowledge for individuals seeking to comprehend the intricacies and significance of these advanced technologies.
Absolutely, the informative content and historical background of X-rays and ultrasound waves enrich our understanding of these technologies, fostering a deeper appreciation for their pivotal roles in healthcare, research, and technological advancements.
I share the sentiment, the detailed explanations and comparative analysis offer readers a comprehensive insight into the fascinating world of X-rays and ultrasound waves, shedding light on their remarkable impact and diverse applications.
The historical background and fundamental properties of X-rays and ultrasound waves, along with their respective frequencies and nature of waves, provide a solid foundation for understanding their significance in technological and medical advancements.
Precisely, the detailed description of the energy, nature, and applications of X-rays and ultrasound waves contributes to a deeper comprehension of their roles and contributions in different domains.
The detailed scientific explanations of X-rays and ultrasound waves, including their energy, nature, and applications, equip readers with foundational knowledge to appreciate the significance of these advanced technologies in our daily lives and healthcare practices.
Absolutely, the informative content and detailed comparisons enhance our understanding of X-rays and ultrasound waves, paving the way for their safe and effective utilization in various scientific, medical, and technological contexts.
The comprehensive explanation of X-rays and Ultrasound waves, and their applications in radiography, ultrasonography, and other areas is insightful. The ionizing capacity of X-rays and its risks should be carefully managed in medical practices.
Absolutely, the comparison table provides a clear understanding of the differences between X-rays and ultrasound waves, shedding light on their distinctive features and applications in various fields.
I agree, the ionizing capacity of X-rays, and the potential risks associated with them, should be closely monitored to ensure safe and effective usage in medical treatments.
The distinction between X-rays and ultrasound waves, including their frequencies, ionizing capabilities, and associated risks, highlights the importance of informed and responsible usage of these technologies in healthcare and beyond.
Indeed, the comparison table and detailed explanations emphasize the critical considerations surrounding the use of X-rays and ultrasound waves, particularly in medical diagnosis and treatments.
The detailed explanations and comparisons of X-rays and ultrasound waves, covering their energy, penetration capabilities, and applications in different technologies and medical practices, broaden our understanding of these essential technologies.
I completely agree, the informative content and in-depth details provide a comprehensive understanding of the uses and potential risks associated with X-rays and ultrasound waves, guiding us in their responsible and effective utilization.
The insights into the ionizing capacity, energy, and distinct applications of X-rays and ultrasound waves serve as valuable knowledge for healthcare professionals, researchers, and technology specialists.
The historical context and scientific explanations of X-rays and ultrasound waves, complemented by their real-world applications, offer a holistic view of their contributions to various fields, particularly in scientific research and medical care.
I share the sentiment, the comprehensive overview and practical examples highlight the significance and versatility of X-rays and ultrasound waves in technological advancements and healthcare practices.
The application of X-rays, UV rays, and IR rays in various technologies and in medical technology has brought several benefits. Its usage in ultrasonography for diagnosis is remarkable.
Indeed, the development and advancements in medical technology have immensely contributed to the use of X-rays and ultrasound waves, benefiting both patients and professionals.
The comparison and contrasts drawn between X-rays and ultrasound waves provide insights into their unique characteristics and applications in healthcare and other fields.