Of all the existing substances, atoms are the building blocks. The nucleus, which is part of an atom, nucleus further has two parts that are protons and neutrons.
The electrons circle the nucleus in orbit. In fact, in addition to electrons and neutrons, there are some subatomic particles present in the nucleus.
Usually, in an atom, most of the space is free and is left empty. The two attractive forces between the nucleus, which is positively charged and the negative ones, which are the electrons, are responsible for maintaining the shape of the atom.
Key Takeaways
- Electrons are negatively charged subatomic particles that orbit the nucleus of an atom.
- Protons are positively charged particles found within an atom’s nucleus.
- The balance between electrons and protons determines an atom’s overall charge and chemical properties.
Electron vs Proton
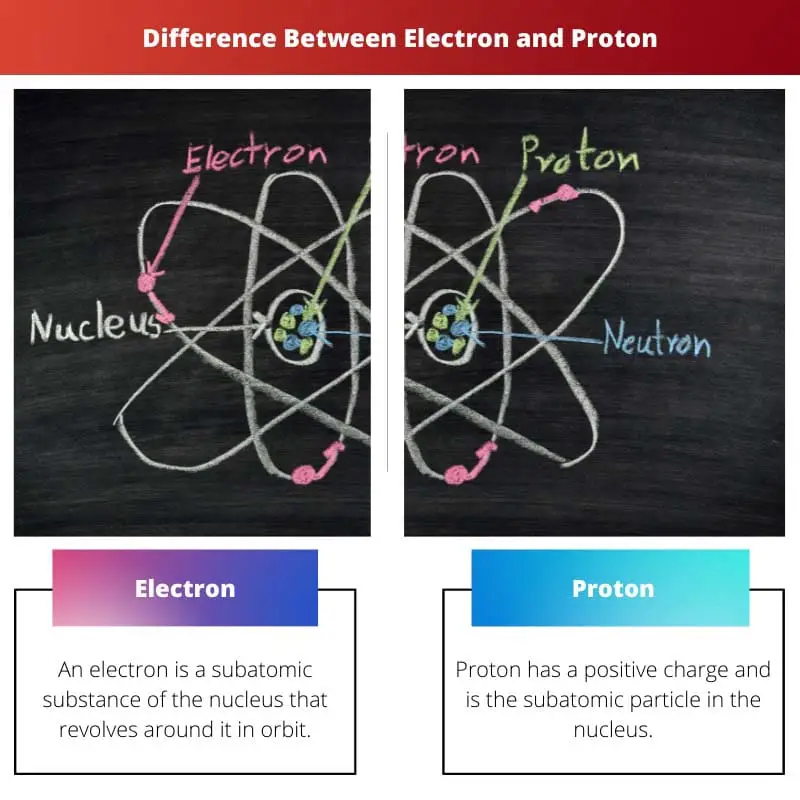
The difference between electrons and a proton is that a proton is just a subatomic substance or particle that is found in the nucleus of an atom, while electrons, on the other hand, are particles that are constantly revolving around the nucleus in orbit. In addition to electrons and neutrons, there are some subatomic particles present in the nucleus.
An electron has a negative electric charge and has the symbol an “e.” Talking about the mass of an electron is 9.1093×10 to the power -31 kg. This mass of electrons makes it the lightest particle of the subatomic.
Electron was discovered for the first time in 1897 by J.J. Thompson. Although, the name of the electron was given by Stoney.
Proton has a positive charge and is the subatomic particle in the nucleus. Proton is denoted by its first alphabet, “p.” When scientists discovered the electron, they did not have any single idea about protons or even the presence of protons.
A positively charged particle was discovered by Goldstein, and that particle was produced from gases. Now, these particles were given the name of anode rays.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Electron | Proton |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | An electron is a subatomic substance of the nucleus that revolves around it in orbit. | Proton has a positive charge and is the subatomic particle in the nucleus. |
| Charge and mass | The charge of an electron is -1, and its mass is 9.1093×10 to the power -31 kg. | The charge of a proton is +1, and its mass is 1.6726×10 to the power -27 kg. |
| Reaction | Electron is involved in chemical reactions. | Proton is not involved in any sort of chemical reaction but might be involved in a nuclear reaction. |
| Movements | The electron has a continuous movement around the nucleus in orbit. | Proton does not move at all. |
| Location in atom | The electron is present around the nucleus. | Proton is present in the atomic nucleus. |
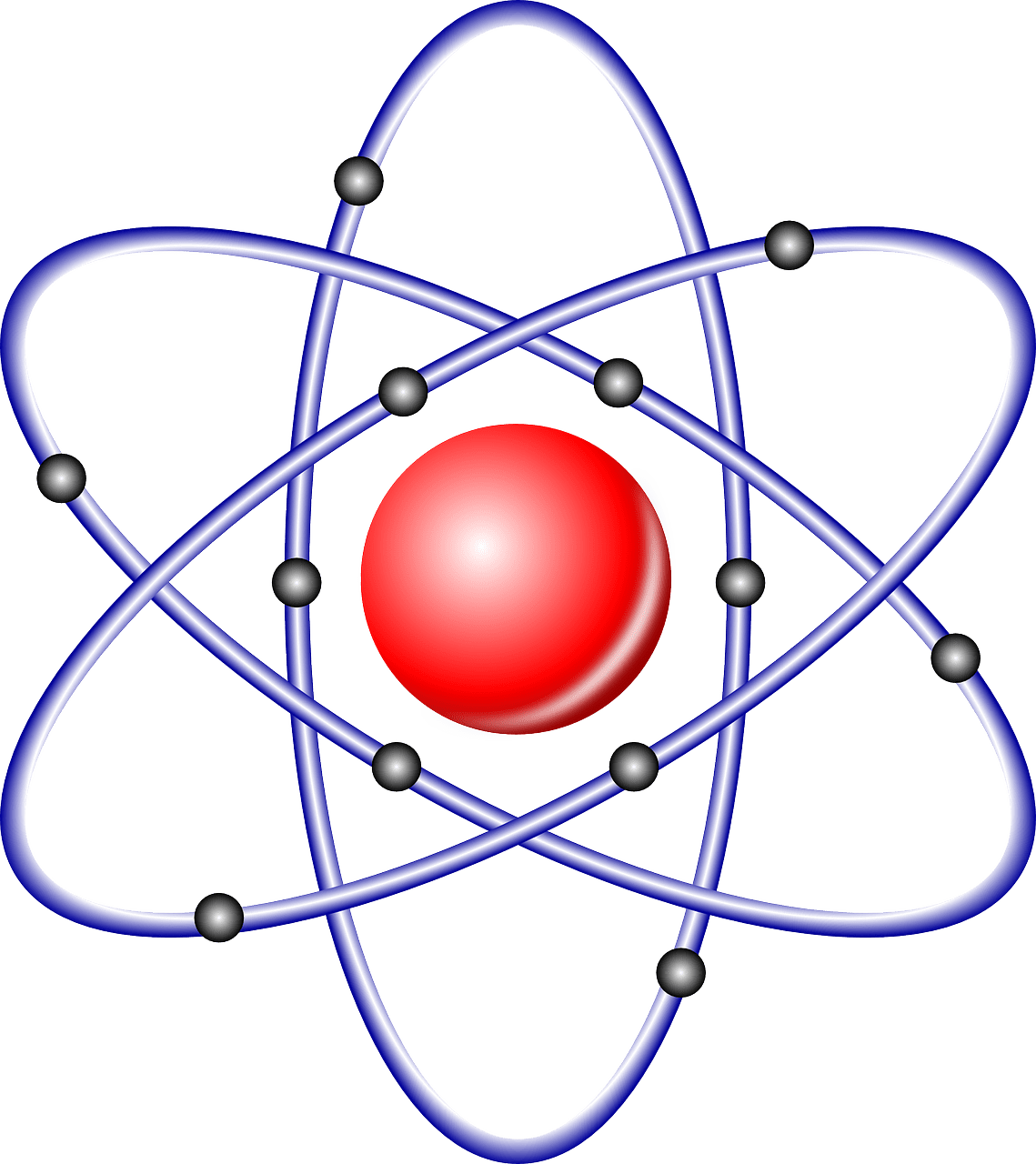
What is Electron?
Electrons are said to be the very first generation or substance of the Lepton family, which is a family of particles. An electron has a negative electric charge and has the symbol an e.
This mass of electrons makes it the lightest particle of the subatomic, and that mass is 9.1093×10 to the power -31 kg. J.J. Thompson was the person who discovered electrons for the very first time in the year 1897.
Its discovery leads to many explanations in electricity, chemistry and chemical bonding, magnetic properties, thermal activities, and many other important phenomena. In an orbital, where they revolve around the nucleus, an electron occurs in pair of electrons.
Each of those pairs has two electrons, both of opposite spins. This arrangement of electrons in an orbital can be given an understandable configuration.
What is Proton?
Protons and neutrons are jointly termed nucleons, and both of these have masses that are approximately equal to one atomic unit. In the nucleus of every single atom, one or even more than one photon is present.
Now the number of protons in each and every nucleus cell is the property of every element that defines it. This is why each element has different atomic numbers because each and every element has its own unique number of protons.
Proton has a different charge to their mass ratio, unlike the electrons, and this depends on the amount of gas used. Finally, in 1917, after many different experiments by several scientists, Rutherford discovered the proton.
The atomic number is the name given to denote the number of protons present in an atom. This is the reason that atomic number is equal to the number of protons an element has in its own nucleus.
Main Differences Between Electron and Proton
- The main difference between an electron and a proton is that an electron is a subatomic substance of the nucleus that revolves around it in orbit, while a Proton has a positive charge and is the subatomic particle in the nucleus.
- The charge of an electron is -1, and its mass is 9.1093×10 to the power -31 kg, while the charge of a proton is +1, and its mass is 1.6726×10 to the power -27 kg.
- Electron is involved in chemical reactions, while Proton is not involved in any sort of chemical reaction but might be involved in a nuclear reaction.
- The electron has a continuous movement around the nucleus in orbit, but Proton does not move at all.
- Electron is present around the nucleus, while Proton is present in the atomic nucleus.
- https://inis.iaea.org/search/search.aspx?orig_q=RN:23085529
- https://www.annualreviews.org/doi/pdf/10.1146/annurev.pc.37.100186.001015

The impact of electron and proton research transcends the scientific realm and permeates various aspects of everyday life, propelling technological progress and innovation.
I concur with your assessment, Nclarke. The breakthroughs arising from subatomic investigations facilitate the evolution of diverse industries and societal domains.
The foundational knowledge elucidated about electrons and protons reinforces the importance of these elementary particles in the architecture of matter and the formulation of natural laws.
I concur, Naomi. The understanding of subatomic constituents enables researchers and scientists to unravel the mysteries of the universe and elucidate the fundamental principles underpinning existence.
The articles provide valuable information regarding the properties and roles of electrons and protons in atoms. It serves as a foundation for understanding various scientific fields such as quantum mechanics, chemistry, and subatomic particle physics.
Indeed, Charlotte. The detailed comparison between electrons and protons enhances our comprehension of their distinctions and significance in atomic structures and reactions.
Both electrons and protons are fundamental particles that play a crucial role in the structure and behavior of atoms. Understanding the properties of these subatomic particles is essential in comprehending the nature of matter and the universe.
I fully agree with you, Georgia. Electrons, with their negative charge, combined with protons, contribute to the stability and characteristics of atomic structures.
Your input is insightful, Georgia. The interactions between electrons and protons are incredibly influential, leading to diverse chemical and physical phenomena.
The historical context of electron and proton discoveries underscores the evolution and refinement of scientific methodologies and the collaborative nature of human scientific endeavors.
Your insight is profound, Thompson. The chronicles of subatomic exploration exemplify the iterative and cooperative nature of scientific exploration, shaping the trajectory of human knowledge and progress.
The elucidation of electron and proton properties has laid the groundwork for profound scientific theories and experimental investigations, fostering a deeper understanding of fundamental physical phenomena.
Well said, Jake. The knowledge derived from the study of these subatomic particles has paved the way for significant advancements in physics, challenging and reshaping scientific paradigms.
I agree with your assessment, Jake. The implications of electron and proton characteristics extend beyond basic atomic constituents and extend to broader concepts of matter and energy.
The historical background of electron and proton discovery is a testament to human curiosity and ingenuity, highlighting the enduring pursuit of knowledge and understanding.
Your perspective is perceptive, Nblake. The evolutionary trajectory of scientific discovery encapsulates the dedication and intellectual rigor of countless scientists and researchers.
The discovery and understanding of electrons and protons have revolutionized scientific knowledge, leading to advancements in numerous technological applications and innovations.
Your observation is astute, Maria. The practical implications of electron and proton research are evident in the development of electronic devices, materials science, and energy technologies.
Absolutely, Maria. The utilization of such fundamental insights has influenced modern technologies and engineering, further shaping our contemporary society.
The fundamental differences and interactions between electrons and protons underscore their pivotal roles in the exploration of the microscopic world and the formulation of scientific principles.
The comparison table provides a concise and clear outline of the distinguishing features and functions of electrons and protons, serving as a valuable reference for scientific discourse and pedagogy.
Your observation is accurate, Lucas. The tabulated presentation enhances the accessibility and understanding of complex scientific concepts for researchers, educators, and students.
I share your sentiments, Lucas. The systematic representation of electron and proton characteristics in the table aids in clarifying intricate scientific nuances and promoting comprehensive learning.