When it comes to heart arrhythmia, it is considered an irregular heartbeat. Heart rhythm problems or simply heart arrhythmias occur when the heartbeat coordinating electrical signals fails to work properly.
Irregularity in a heartbeat is mainly due to faulty signaling. In general, a heart arrhythmia can be grouped by the heart rate speed into bradycardia and tachycardia.
Among the classification of tachycardia, Afib and Aflutter are two of their kinds. In this article, the main focus is on differentiating Afib and Aflutter.
Key Takeaways
- AFib is an irregular and rapid heart rhythm, while AFlutter is a regular but rapid heart rhythm.
- AFib is more common than AFlutter and can last longer, while AFlutter is less common and lasts for shorter periods.
- Both AFib and AFlutter can increase the risk of stroke and heart failure.
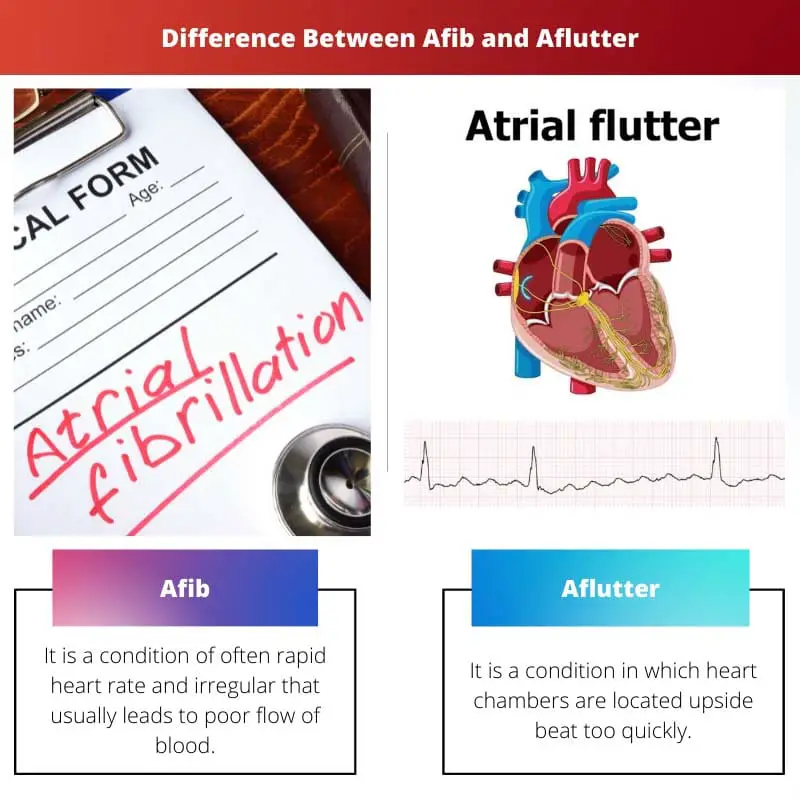
Afib vs Aflutter
AFib is a condition that is characterized by a rapid and irregular heartbeat, where the heart’s upper chambers quiver instead of beating effectively. AFlutter is a heart condition characterized by a fast but regular heartbeat, with the atria beating more quickly than the lower chambers.

Afib is a condition related to the heart in which an abnormal or irregular heart rhythm is developed. The origination point of this irregularity is atria.
Mechanical and electrical activity in the atrium leads to irregularity, although this is unrelated to the activity of the ventricles.
Aflutter is less common as well as secondary to an electrical pathway of abhorrence in the Atria. It would be considered more severe due to its deterioration into more threatening arrhythmias.
The Atria will tend to be beaten in Aflutter at 250 –300 bpm.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Afib | Aflutter |
|---|---|---|
| Interpretation | It is a condition of rapid heart rate and irregular that leads to poor flow of blood. | It is a condition in which heart chambers are located upside beat too quickly. |
| Also called | AF or Atrial fibrillation | Atrial flutter |
| Type | Chronic (be lifelong or simply last for years) | Critical (needs emergency care) |
| Risk factors | Family history, obesity, thyroid disease, and age. | Smoking, diabetes, lung disease, and past heart attack. |
| Complications | Blood clots and heart failure | High blood pressure and some valvular heart disease |
What is Afib?
In the heart, the Afib condition can lead to blood clots. It increases the risk of failure of heart stroke and other complications related to the heart. During Afib, the atria or heart chambers can lead to beating irregularly and chaotically.
For many people, there might be no symptoms related to Afib. This is because the episodes of Afib might come and go or just be persistent. However, it might cause weakness, shortness of breath, palpitations, or a pounding heartbeat.
Although it is not life-threatening while a medical condition that is serious and to prevent stroke requires proper treatment.
Seek immediate medical help in case of chest pain because it means a heart attack might occur. Afib might be long-standing persistent, occasional, persistent, and permanent.
Prevention is much better compared to treatment. Thus, quitting smoking and having a nutritious diet can prevent the condition of Afib. Treatment for Afib might be consisting therapy to reset the catheter procedures and heart rhythm to block faulty heart signals.

What is Aflutter?
When Aflutter first occurs, it is linked with a fast heart rate and grouped as a type of supraventricular tachycardia. It is characterized by an instantaneous onset, heart rhythm as regular abnormal on an ECG in which the first heart rate is mentioned.
Although this heart rhythm is abnormal occurs in individuals with the disease of cardiovascular and diabetes mellitus. In people, it might occur spontaneously with otherwise normal hearts. Also, with not a stable rhythm.
Supraventricular tachycardia with 150 beats per minute ventricular heart rate is suggestive of Aflutter. Adenosine administration in the vein can help medical personnel differentiate between Aflutter and other kinds of supraventricular tachycardia.
In 1920, British physicians first identified Aflutter as a medical condition, namely Sir Thomas Lewis and colleagues. Aflutter Is the most common supraventricular tachycardia of pathologic but occurs at a lower rate than one-tenth of the Afib.

Main Differences Between Afib and Aflutter
- Sensations of fluttering, fast or pounding heartbeat, reduced ability to exercise, weakness, and chest pain are the symptoms of Afib. Meanwhile, symptoms of Aflutter are shortness of breath, pressure in the chest, fatigue, and dizziness.
- When it comes to prevention, Afib can be prevented by limiting or avoiding caffeine and alcohol, getting regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight. Conversely, Aflutter can be prevented by eating a nutritious diet and quitting smoking.
- Tests like chest X-rays, event monitors, blood tests, and stress tests are used to diagnose Afib. On the flip side, Aflutter can be diagnosed by Holter monitor, echocardiogram, electrophysiology studies, and electrocardiograms.
- Medications required to treat Afib are digitalis glycosides (strengthen heart contractions) and blood thinners (prevent from forming blood clots). On the contrary, calcium channel blockers (relax arterial muscles) and beta-blockers (decrease heart rate) are medications to treat Aflutter.
- Possible causes of Afib are coronary artery disease, sleep apnea, viral infections, and heart valve problems. On the other hand, non-cardiac surgery, lung blood clots, chronic lung disease, and enlarged heart chamber are causes of Aflutter.
References
- https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/abs/10.1161/circoutcomes.114.001263
- https://heart.bmj.com/content/94/11/1394.short

The content is well-researched and comprehensive
This is fascinating! Thanks for sharing
Great article! Very educational and informative
Informative! More people should know about this
Very interesting, thank you!
This article was enlightening, thank you