All organisms are made up of cells, the primary living unit. Some are composed of single cells, while others are composed of multiple cells.
Key Takeaways
- Archaea and bacteria are two distinct groups of single-celled microorganisms, differing in their cellular structures, metabolic pathways, and evolutionary history.
- Archaea have unique cell membrane structures and are more closely related to eukaryotes than bacteria, with some species able to thrive in extreme environments such as high temperatures or salinity.
- Bacteria are more diverse and widespread than archaea, with many species playing important roles in human health, industry, and the environment, while others can cause disease.
Archaea vs Bacteria
The difference between Archaea and Bacteria is that the cell wall of Archaea does not have a polymer comprising of amino acids and sugars called peptidoglycan. The cell wall of Bacteria, on the hand, has a mesh-like peptidoglycan coating.

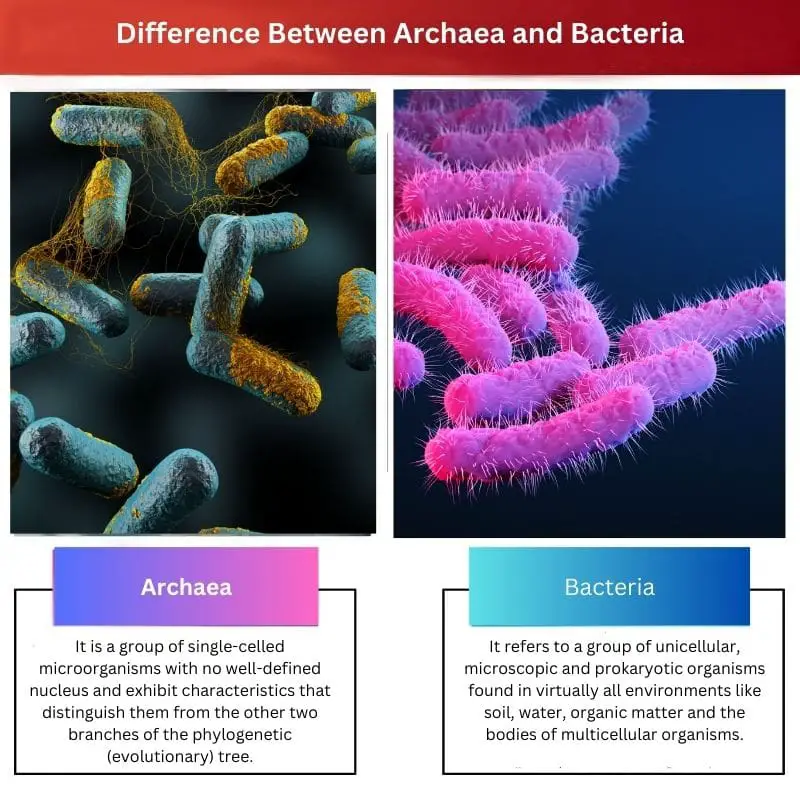
Archaea is a group of prokaryotes whose members exhibit specific unique physical, physiological and genetic features distinguishing them from bacteria on the one hand and eukaryotes on the other.
On the other hand, bacteria are a group of unicellular, microscopic organisms that can survive in virtually all environments, including soil, water, organic matter and the bodies of multicellular organisms.
Also, the plasma membrane of Archaea has ether-linked (one atom of oxygen bonded with two aryl or alkyl groups) lipids. At the same time, the plasma membrane of Bacteria uses ester-linked (one oxygen atom bonded with two hydrocarbon groups) lipids.
Comparison Table
| Parameter of Comparison | Archaea | Bacteria |
|---|---|---|
| Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) | Three | One |
| Reproduction | Budding, binary fission and fragmentation. | Produces spores so that they can survive for several years in a variety of conditions-favourable and unfavourable. |
| Found in | Unusual and extreme conditions like deeper regions of oceans, hot springs, swamps etc. | Almost everywhere, like the earth’s crust, organic matter, water bodies, bodies of humans and animals and so on. |
| Cell Wall | Composed of an S-layer or pseudo peptidoglycan. | They are composed of peptidoglycan accompanied by muramic acid. |
| Major groups | Halophiles, Methanogens, Thermoacidophiles. | Gram-negative and Gram-positives. |
What is Archaea?
It is a group of single-celled microorganisms with no well-defined nucleus and exhibit characteristics that distinguish them from the other two branches of the phylogenetic (evolutionary) tree.
When it was first discovered, it was put into the category of bacteria due to their resemblances in size and shape and was named Archaebacteria. However, eventually, it was found that Archaea exhibited certain features of Eukaryotes which were not present in bacteria.
Besides, it is believed that one of the ancestors of the present Archaea had given birth to Eukarya. Consequently, the category of Archaebacteria became obsolete.
The term Archaea is of Greek origin. It comes from archaios which means ‘primitive’, ‘archaic’ or ‘ancient’.
The Archaea may be aquatic or terrestrial microorganisms. They show a diversity of shapes, including spherical, rod-like, and spiral forms.
Some survive on oxygen and produce methane as an end product, whereas others do not. They reproduce asexually by various mechanisms, including binary fission, fragmentation and budding.
What is Bacteria?
It refers to a group of unicellular, microscopic and prokaryotic organisms found in virtually all environments like soil, water, organic matter and the bodies of multicellular organisms.
The four basic shapes of bacteria are bacillus (rod-like), vibrio (comma-shaped), coccus (spherical), and spirillum (spiral). Like Archaea, there is no well-defined nucleus in bacteria.
Apart from the genomic DNA, single chromosome or circular DNA, many bacteria contain another small, circular DNA that resides outside the genomic DNA. These smaller DNA are known as plasmids.
Based on the structure of their cell wall and their reaction to gram stain (staining with a violet dye to identify the species of bacteria), bacteria are classified into two main groups- gram-positive and gram-negative.
Gram-positive bacteria turn purple during the gram-staining experiment and have a thick layer of peptidoglycan in their cell walls. Gram-negative bacteria, on the other hand, exhibit a pink colour when stained with violet dye and possess a thin layer of peptidoglycan.
Although some bacteria can cause food poisoning and infectious diseases in human beings, most of them are harmless. Many bacteria are helpful as well.
Bacteria are also used in various industrial processes, especially in the food industry. For example, producing cheeses, yoghurt and pickles is impossible without bacterial reactions.
Main Differences Between Archaea and Bacteria
- Both Archaea and Bacteria are single-celled prokaryotes. But Archaea shows specific characteristics of Eukaryotes as well.
- Archaea can exist in extreme and unusual conditions like salty water, hot springs, deeper regions of oceans, marshes and the gastrointestinal tract of human beings. Bacteria, on the other hand, are almost omnipresent.
- Both Archaea and Bacteria procreate asexually, but their mechanisms are different. Archaea procreate by the mechanisms of budding, binary fission and fragmentation.
- The cell wall of Archaea is not made up of peptidoglycan. It comprises simpler connecting subunits called the S-layer or pseudo peptidoglycan.
- The plasma membrane of Archaea has lipids covered with hydrocarbons which are sometimes branched and form monolayers. These lipids have ether bonds that connect the glycerol backbones.
- https://www.nature.com/articles/nature08465
- https://academic.oup.com/femsec/article-abstract/39/1/1/535284

The comparison table provided a clear comparison showing the differences between Archaea and Bacteria.
Yes, it was very helpful and easy to understand.
This article is full of well-explained information about Archaea and Bacteria.
I think so too. It was very insightful.
The writer needs to consider a more neutral tone to avoid any negative bias towards any of the groups.
The comparison is balanced and scientific.
I don’t think it is biased. It simply presents the differences between the two groups.
This is the best explanation about Archaea and Bacteria that I’ve ever read.
I learned a lot from it.
Agree! It’s a really well-written and comprehensive article.
The article is very interesting and clearly explains the differences between these two types of organisms.
Yes, and it’s presented in an engaging manner.
I agree, it provides a thorough understanding of the topic.
This article is very educational and well-written.
The article is overly scientific and feels like a lecture. It could use a bit of humor to lighten the mood.
I enjoy the scientific approach. It’s informative and engaging.
Sometimes, being scientific is necessary for educational purposes.
I found this article to be quite dry and unengaging. It could use some more entertaining elements.
I appreciate the serious and informative tone. Entertaining elements aren’t always necessary.
I liked the detailed content of this article. It really helped me to understand the differences between Archaea and Bacteria.
This is an excellent informative comparison between Archaea and Bacteria. It provided me with a lot of new information to learn from.
I agree, the article was very informative and detailed.