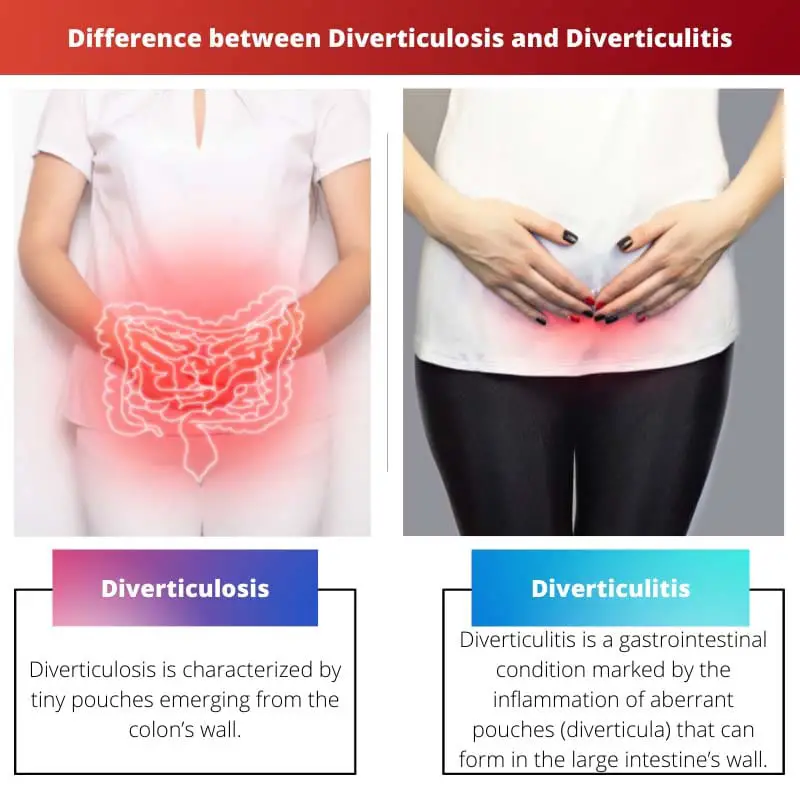
The human intestine is a long organ that is split into two portions for convenience of diagnosis: the small intestines and then the large bowel or colon. Diverticulosis is defined by tiny pouches emerging from the colon’s wall.
Diverticulitis is a condition that occurs as a result of an infection. Diverticulitis is more severe than other types of diverticulitis because the infection can progress to additional complications.
Key Takeaways
- Diverticulosis is the formation of small pouches in the colon, while diverticulitis is the inflammation or infection of these pouches.
- Diverticulosis causes no symptoms, but diverticulitis can result in abdominal pain, fever, and changes in bowel habits.
- Treatment for diverticulosis focuses on preventing complications, whereas diverticulitis requires antibiotics or surgery in severe cases.
Diverticulosis vs Diverticulitis
Diverticulosis is a medical condition in which the colon has diverticula, which are numerous pouches that are not inflamed. Diverticulitis is also known as colonic diverticulitis and is a gastrointestinal illness that is noticeable by inflammation of aberrant pouches forming on the large intestine wall.

Diverticulosis is a condition in which the colon has numerous pouches (diverticula) that are not inflamed.
Outpockets of the colonic mucosa and submucosa are produced by muscle layer defects in the colon wall and can be exacerbated by a low-fibre diet that alters the microbiota and induces low-grade inflammation.
Diverticulitis, particularly colonic diverticulitis, is a gastrointestinal illness marked by inflammation of aberrant pouches (diverticula) that can form in the large intestine wall.
Lower abdomen discomfort with a rapid onset is common, although it can gradually develop over several days. It might create a lot of pain in your stomach.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Diverticulosis | Diverticulitis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Diverticulosis is characterized by tiny pouches emerging from the colon’s wall. | Diverticulitis is a gastrointestinal condition marked by the inflammation of aberrant pouches (diverticula) that can form in the large intestine’s wall. |
| Symptoms | cramping, bloating, flatulence, and irregular defecation. | abdominal pain of sudden onset, have elevated C-reactive protein, and a high white blood cell count. |
| Location | The lining of the intestine | Lower abdomen |
| Diagnosis | Clinical blood tests; serum iron concentrations, OZHSS, average haemoglobin content in erythrocytes; faecal occult blood analysis; general urine analysis | Blood test and urine test, Medical history analysis, Physical examination, Colonoscopy, CT scan, Lower GI series |
| Causes | Pressure builds in your colon and pushes on the lining when you experience muscular spasms or strain (as when you have a bowel movement). | Low-fibre diets increase pressure on the colon to force stool out, causing stool materials to lodge in the diverticula, leading to infection. |
| Risk factors | Due to excessive obesity, Excessive consumption of fat and red meat, cigarette smoking. | Obesity, smoking, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs) |
| Risk of cancer | High risk of cancer | Minor risk of cancer |
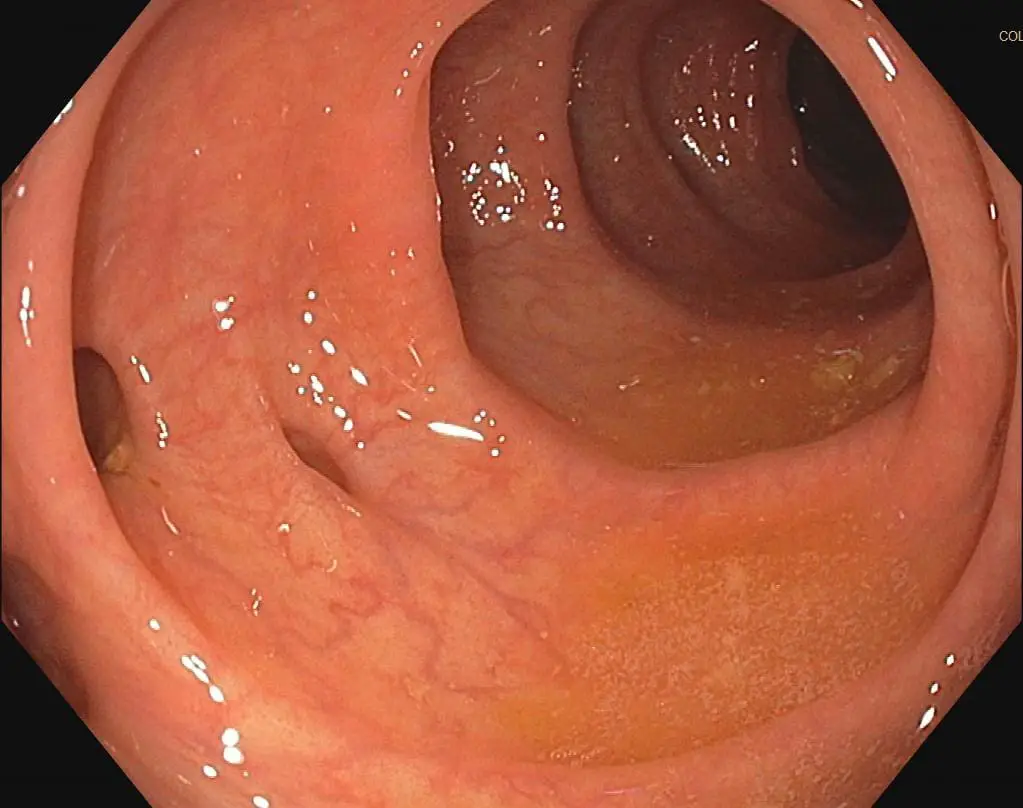
What is Diverticulosis?
Diverticulosis is most commonly found in the sigmoid colon, which is prone to high pressure. In the United States, the left side of the colon is more afflicted, but in Asia, the right side is more commonly affected.
The diagnosis is frequently made during a regular colonoscopy or as a result of an unintentional discovery during a CT scan.
Diverticular illness can cause painless rectal bleeding that appears as bright red blood in the rectum. Acute lower gastrointestinal bleeding is most commonly caused by diverticular bleeding.
However, it is believed that 80% of these instances are self-limiting and do not require treatment.
Although the low-fibre explanation of diverticulosis is the most popular, it has yet to be proved, according to the National Institutes of Health in the United States.
Diverticulosis is not an issue in and of itself, as the pouches are innocuous and seldom produce symptoms.
Many people who have diverticulosis have little or no symptoms and may not require therapy. Colonic stimulants should be avoided if at all possible.
Treatments that induce hard stools, constipation, or straining, such as certain colon cleaners, are not suggested.
What is Diverticulitis?
Diverticulitis is more severe than other types of diverticulitis because the infection can progress to additional complications. In around 1 out of every 5 to 1 out of every 7 instances of diverticulosis, diverticulitis develops.
Diverticulitis can have a variety of reasons. Obesity, inactivity, smoking, a family history of the illness, and the use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications are all potential risk factors (NSAIDs).
It’s uncertain if a low-fibre diet is a risk factor. Diverticulosis is a condition in which pouches in the large intestine aren’t inflamed.
Inflammation, which is caused by a bacterial infection, affects 10% to 25% of people at some point in their lives.
CT scans are commonly used to diagnose the condition, although blood tests, colonoscopies, and a lower gastrointestinal series may also be helpful. Irritable bowel syndrome is one of the many possibilities.
Diverticulitis is caused by a combination of genes and environmental factors, with around 40% of cases attributable to genes and 60% due to environmental factors.
Arterial hypertension and immunosuppression are two conditions that enhance the likelihood of developing diverticulitis. Another risk factor is obesity. Vitamin D deficiency has been linked to an increased incidence of diverticulitis.
Main Differences Between Diverticulosis and Diverticulitis
- Diverticulosis is characterized by tiny pouches emerging from the colon’s wall, whereas, Diverticulitis is a gastrointestinal condition marked by the inflammation of aberrant pouches (diverticula) that can form in the large intestine’s wall.
- The symptoms of Diverticulosis are cramping, bloating, flatulence, and irregular defecation, whereas the symptoms of Diverticulitis are abdominal pain of sudden onset, elevated C-reactive protein, and a high white blood cell count.
- Diverticulosis occurs in the lining of the intestine, while Diverticulitis occurs in the lower abdomen.
- In Diverticulosis, the risk of cancer is high, whereas in Diverticulitis. The risk of cancer is minor.
- Pressure builds in your colon and pushes on the lining when you experience muscular spasms or strain (as when you have a bowel movement), causing Diverticulosis, whereas Low-fiber diets increase pressure on the colon to force stool out, causing stool materials to lodge in the diverticula, leading to infection causes Diverticulitis.
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Diverticulosis
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Diverticulitis
- https://iffgd.org/gi-disorders/diverticulosis-and-diverticulitis/

Although diverticulosis is asymptomatic, it’s important to recognize the potential risks and understand how diverticulitis may develop.
Agreed, the article does an excellent job of explaining the progression from diverticulosis to diverticulitis and the associated health risks.
The detailed explanation of diverticulosis and diverticulitis is incredibly helpful, especially in understanding the causes and symptoms associated with each condition.
Absolutely, I found the information about the causes and symptoms to be particularly enlightening. A great read overall!
This article was very informative and gave a detailed explanation of diverticulosis and diverticulitis. It’s important to be aware of the symptoms and differences between the two conditions.
I found the comparison table particularly helpful in understanding the distinctions between diverticulosis and diverticulitis.
I completely agree! It’s crucial to understand these gastrointestinal conditions for early diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
I’ve heard about diverticulosis before, but this article really helped me understand the specific symptoms and treatments.
Yes, it’s great to have comprehensive information on these conditions to raise awareness and promote proactive health measures.
I appreciate that the article delves deeper into the risk factors and diagnosis methods for diverticulitis, providing a well-rounded view of the condition.
The article sheds light on the key differences between diverticulosis and diverticulitis. It’s crucial to have this knowledge for better health management.
Absolutely, the comparisons and detailed descriptions are invaluable in understanding these conditions. Well-written and informative post.
The comparison between diverticulosis and diverticulitis was very clear, making it easier to distinguish the two conditions.
The informative content about diverticulosis and diverticulitis is presented in a clear and engaging manner, offering valuable insights into these gastrointestinal conditions.
The comparison table was especially useful in summarizing the key distinctions between diverticulosis and diverticulitis. A well-structured and enlightening article!
I appreciate the thorough explanation of diverticulitis and its risk factors. It’s a helpful resource for those seeking to understand these conditions.