Poblanos and Jalapenos are two of the most popular chillies in Mexico. They’re kitchen classics that can be found in sauces, salsas, and a variety of other dishes.
But, aside from their purposes, these two peppers are strikingly similar. Is one more powerful than the other? What’s the difference in flavour between the two? Is it somehow possible to swap one for the opposite?
Key Takeaways
- Jalapenos are smaller, spicier peppers, while poblanos are larger and milder in flavor.
- Poblanos are commonly used in Mexican cuisine for stuffed dishes, whereas jalapenos are more versatile in cooking.
- Jalapenos have a vibrant green color and smooth skin; poblanos have a darker green color and wrinkled skin.
Jalapeño vs Poblano
Jalapeno is a small and hot type of pepper that is used in Mexican cuisine and has a bright and slightly sweet flavour. It is used in spicy dishes, such as salsas and chilli. Poblano peppers, which are also a type of pepper used in Mexico, are used in milder dishes, such as chiles rellenos.

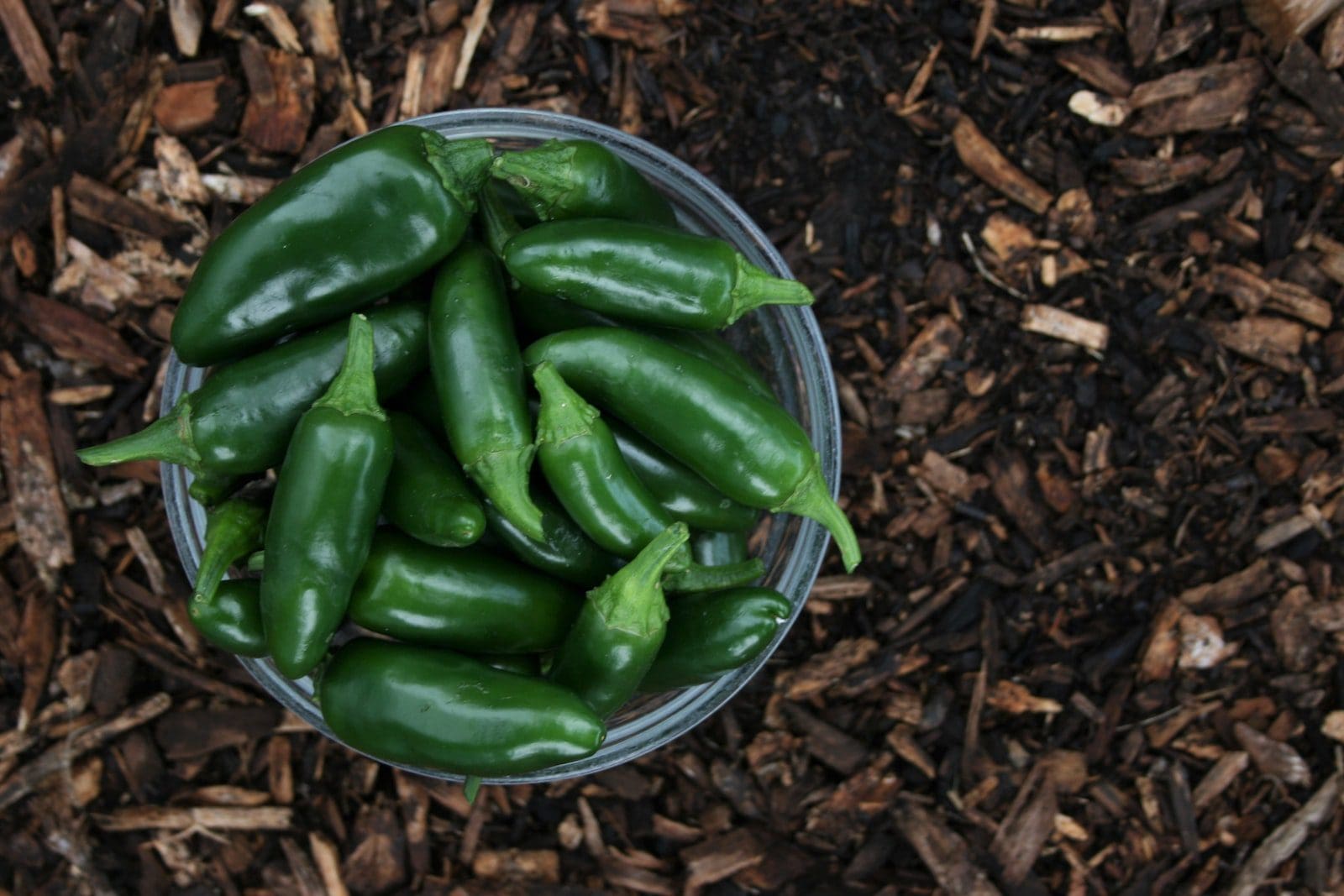
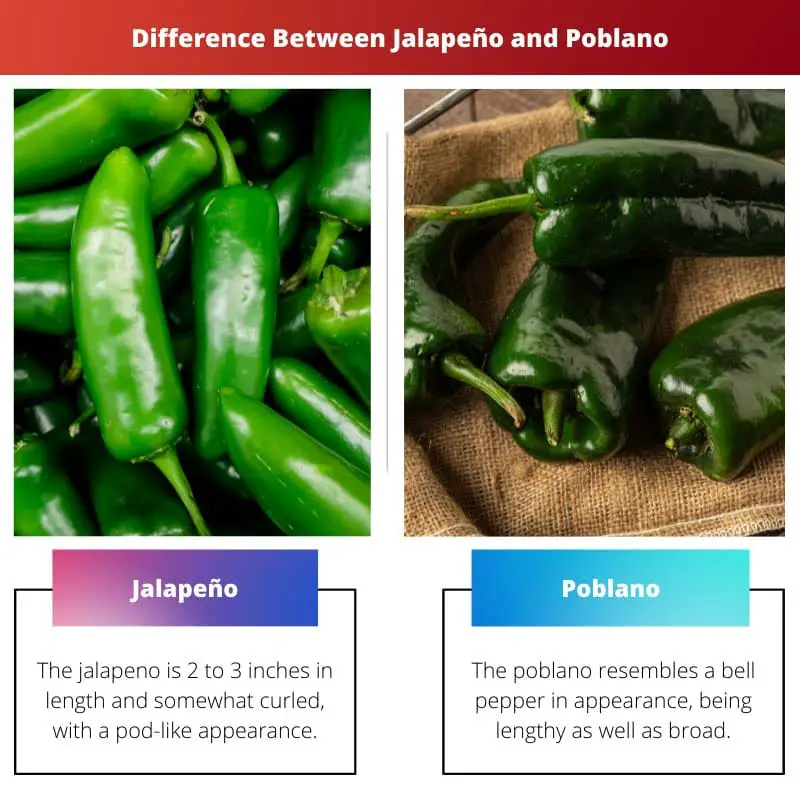
Jalapeno is 2 to 3 inches in length and somewhat curved, with a pod-like appearance. It has a distinct chilli pepper appearance.
Jalapenos are used in more traditional salsas, and they also go well with leafy veggies as a lettuce or sandwich topping. It’s a Capsicum annuum hybrid with a moderate chilli pepper pod kind.
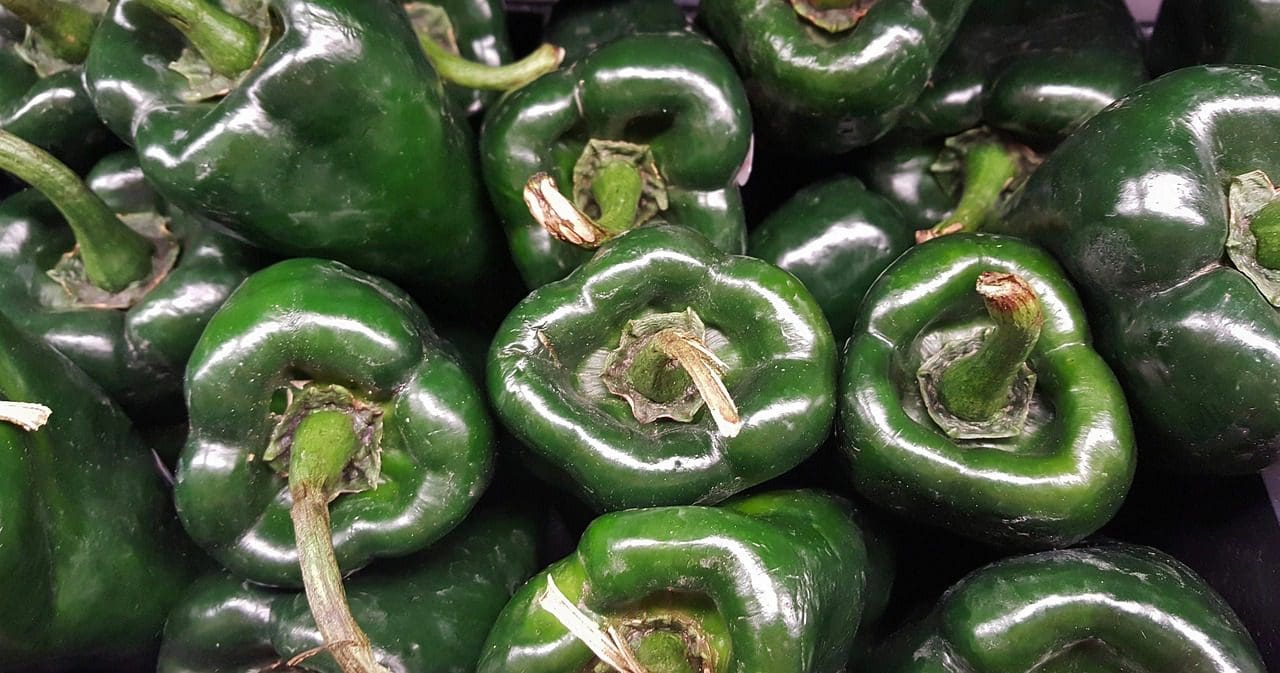
The poblano, on the other side, resembles a bell pepper in appearance, being long (three to 4 inches) and broad.
Poblanos form one of the holy trinity of Mexican chillies utilized in deep and gritty mole sauces, and they’re known as ancho peppers once dehydrated.
The poblano (Capsicum annuum) is a moderate chilli pepper that comes from the Mexican state of Puebla.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Jalapeño | Poblano |
|---|---|---|
| Shape | The jalapeno is 2 to 3 inches in length and somewhat curled, with a pod-like appearance. It has a distinct chili pepper appearance. | The poblano resembles a bell pepper in appearance, being lengthy (up to 4 inches) as well as broad. |
| Taste | The flavor of jalapenos is grassier and livelier. Jalapenos are used in more traditional salsas, and they also go well with leafy veggies as a snack or sandwich topping. | Poblanos have quite a flavor that is earthy and somewhat smoky. |
| Place of Origination | Jalapenos are predominantly grown in Xalapa, Veracruz, although they may also be found in Delicias, Chihuahua, Sonora, and other parts of Mexico. | Poblanos are indigenous to the Mexico’s state of Puebla. |
| Fruits | The length of jalapenos is comparable, but not the breadth. They are not particularly wide and are sometimes known as “chile Gordo.” | The flowers of the poblano plants grow to be just about two to three inches big and thick, and thus are known as “chile ancho” or “wide chile.” |
| Ripe and Unripe | Green jalapenos are unripened, whereas blood-red jalapenos are mature. | The matured poblano is deep brown, nearly black in hue, whereas the juvenile chile is purplish green. |
What is Jalapeño?
It’s a Capsicum annuum hybrid with a moderate chilli pepper pod kind.
A ripe jalapeno chilli measures 5–10 cm in length and has a spherical, firm, glossy flesh that measures 25–38 mm (1–11+12 in) in width. It will have a pungent flavour range of 3,500 to 8,000 Scoville heat values.
It is commonly harvested and enjoyed whilst still green, but it is also permitted to fully mature and turn red, orange, or yellow on rare occasions.
It has a larger range of flavours and is gentler than that of the Serrano pepper.
Jalapeno plants come in a wide range of varieties for both personal and business purposes.
The large proportion falls into one of four subgroups: F1 variants (parent seedlings have indeed been hand-emasculated and cross-breed to define reliable progeny with hybrid vigour).
About 2% of the section devoted to jalapeno production in the United States is seeded with F1 hybrids, which generate the greatest and most consistent harvests but cost 25 times as much as open-pollinated seeds.
F2 hybridization yields identically to F1 hybrids.
Nevertheless, some F1 variants are developed using hereditary male sterility to remove the need for hand-pollination, lowering production costs but diminishing output by 25% in the F2 plants.

What is Poblano?
The poblano (Capsicum annuum) is a moderate chilli pepper that comes from the Mexican state of Puebla. It is known as ancho or chile ancho when dried, derived from its Spanish term ancho.
It is indeed famous in poblano chiles Rellenos, where it’s picked fresh and baked.
Although poblanos have a modest flavour, they could have a lot of heat on occasion and without warning. The heat level of various chillies from the very same plant has been known to vary significantly.
The mature red poblano is substantially spicier and tastier than that of the green poblano, which is far less ripened.
The mulato is a tenuously connected type that is denser, sweeter in flavour and has a thicker consistency.
The pasilla pepper might be mistakenly referred to as a “poblano,”, especially in the United States, but that is not the same as a genuine poblano pepper.
Poblanos thrive best in resilience zones 10–12, with only a soil pH of 7.0 to 8.5. They appreciate direct sunlight and may need extra assistance again for maturing fruits during the late fall harvests.
From seed to harvesting, a poblano requires about 200 days and needs soil conditions of at least 64 degrees Fahrenheit (18 degrees Celsius) to sprout.

Main Differences Between Jalapeño and Poblano
- The jalapeno is 2 to 3 inches in length and somewhat curled, with a pod-like appearance. It has a distinct chilli pepper appearance. On the other hand, The poblano resembles a bell pepper in appearance, being lengthy (up to 4 inches) as well as broad.
- The flavour of jalapenos is grassier and livelier. Jalapenos are used in more traditional salsas, and they also go well with leafy veggies as a snack or sandwich topping. Poblanos have quite a flavour that is earthy and somewhat smoky.
- Jalapenos are predominantly grown in Xalapa, Veracruz, although they may also be found in Delicias, Chihuahua, Sonora, and other parts of Mexico. Whereas, Poblanos are indigenous to Mexico’s state of Puebla.
- The length of jalapenos is comparable, but not the breadth. They are not particularly wide and are sometimes known as “chile Gordo.” The flowers of the poblano plants grow to be just about two to three inches big and thick and thus are known as “chile ancho” or “wide chile.”
- Green jalapenos are unripened, whereas blood-red jalapenos are mature. On the other hand, The matured poblano is deep brown, nearly black in hue, whereas the juvenile chile is purplish green.

The characteristics of both jalapenos and poblanos make them essential elements in Mexican cuisine. Jalapenos are smaller and spicier, whereas Poblanos are larger and milder in flavor. This article provides a comparison of the two kinds of peppers, focusing on their sizes, tastes, place of origination, and other parameters.
Courtney18, your comment is really helpful and adds to the understanding of the topic. Thanks for sharing your insights.
This is a very informative piece. It effectively outlines the differences between Jalapenos and Poblanos, shedding light on their distinct characteristics. The comparison table is particularly useful in understanding the contrast between the two types of peppers.
This article offers a comprehensive analysis of Jalapenos and Poblanos, highlighting their differences in shape, taste, and place of origination. It is a valuable resource for individuals seeking to learn more about these peppers.
The comparison table in the article provides a clear overview of the variations between Jalapenos and Poblanos. This detailed analysis enhances the understanding of these peppers and their distinct attributes.
The in-depth comparison of Jalapenos and Poblanos in this article is quite informative. It elucidates the unique characteristics of these peppers, making it a valuable read for those interested in Mexican culinary ingredients.
I couldn’t agree more, Dan69. The detailed comparison provides a holistic view of Jalapenos and Poblanos, offering valuable information for cooking enthusiasts.
Dan69, your observation on the informative nature of the article is insightful. It emphasizes the importance of understanding the nuances of different peppers in culinary applications.
The comprehensive comparison between Jalapenos and Poblanos provides a clear understanding of their differences. This article effectively highlights the distinctive features of each pepper, which is essential for anyone interested in Mexican culinary ingredients.
I agree, Jcox. The detailed comparison of the two peppers is beneficial for individuals seeking to expand their knowledge of Mexican cuisine.
Jcox, your perspective on the significance of understanding the features of Jalapenos and Poblanos is quite perceptive. It demonstrates the importance of recognizing the unique properties of culinary ingredients.
The article provides a thorough analysis of Jalapenos and Poblanos, delineating the differences in their characteristics and uses. It is an informative piece for anyone interested in Mexican cuisine and culinary ingredients.
I completely agree, Millie Hunter. The detailed analysis of Jalapenos and Poblanos makes this article a valuable reference for individuals keen on expanding their knowledge of culinary components in Mexican cuisine.
Millie Hunter, your comment effectively captures the informative nature of the article. It serves as an enlightening resource for individuals passionate about culinary exploration.
The detailed comparison of Jalapenos and Poblanos contributes to a better understanding of these peppers and their culinary applications. This article serves as a valuable reference for anyone looking to explore Mexican cuisine.
The article offers valuable insights into the differences between Jalapenos and Poblanos, focusing on their shapes, tastes, and place of origination. It is evident that both peppers have unique properties that make them suitable for different culinary applications.
Sonia64, your observation on the unique properties of Jalapenos and Poblanos is quite insightful. It’s interesting to note how these differences contribute to their varied uses in Mexican cuisine.
The article effectively highlights the characteristics of Jalapenos and Poblanos, providing useful information on their tastes, shapes, and origins. It serves as an insightful resource for individuals interested in culinary ingredients.