Coenzymes are essential for carrying out different reactions in our bodies. Coenzymes can be considered helper molecules that help in chemical reactions.
Key Takeaways
- NAD (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) is a coenzyme that acts as an electron carrier in metabolic reactions, while FAD (flavin adenine dinucleotide) is another coenzyme that carries electrons in redox reactions.
- NAD is involved in energy metabolism and is used in both catabolic and anabolic reactions, while FAD is involved in oxidative reactions in the mitochondria.
- NAD is derived from niacin (vitamin B3), while FAD is derived from riboflavin (vitamin B2).
NAD vs. FAD
NAD is a type of coenzyme. Living cells can have NAD. Only one hydrogen atom can be accepted by NAD. There are two nucleotides in NAD that are combined together. NAD can be used in the discovery of drugs. Two hydrogen atoms can be accepted by FAD. There are four states of FAD. There are two parts of FAD which are combined together.
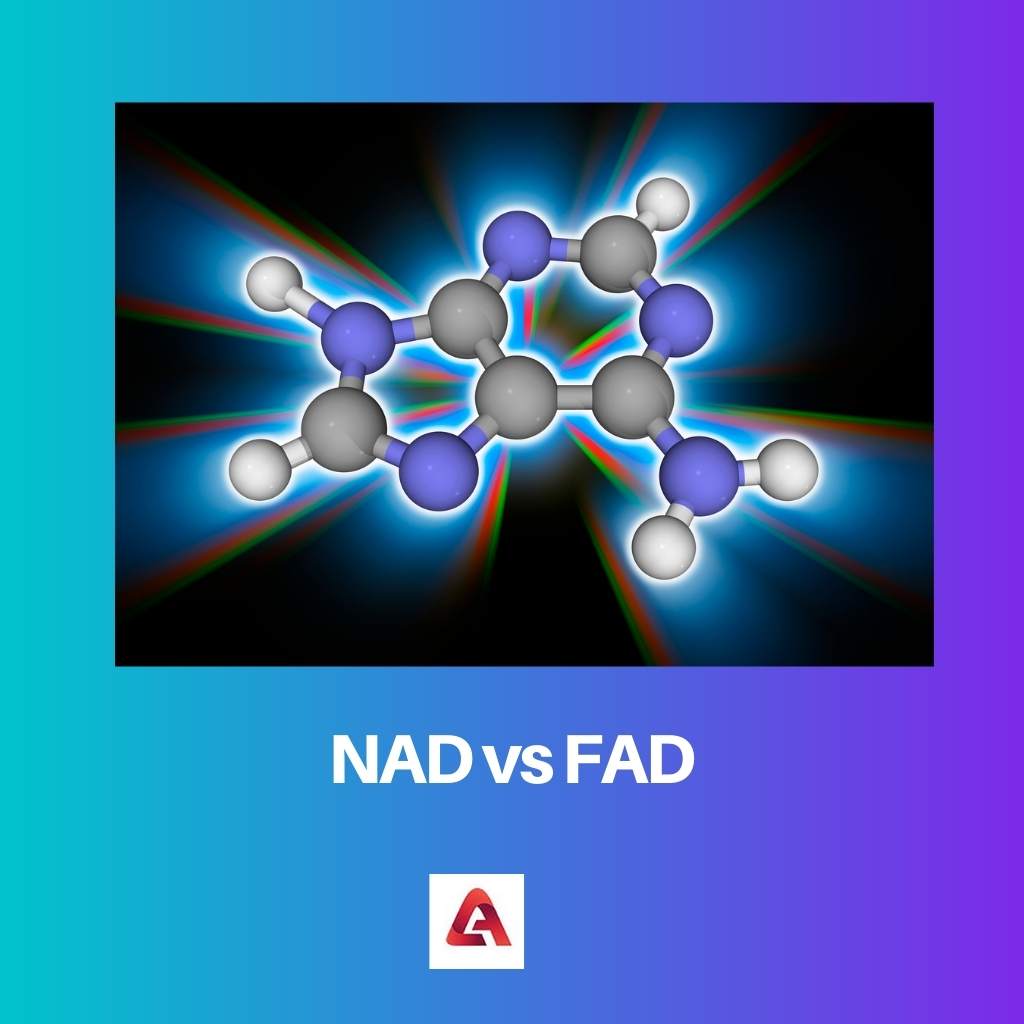
It is found in all the cells which are living. As the name dinucleotide suggests, it has two nucleotides joined by phosphate groups. NAD can be found in two forms, i.e., oxidized and reduced condition or state.
FAD is Flavin adenine dinucleotide, a cofactor that is the type of coenzyme, and it is involved in various enzymatic reactions that are necessary for metabolism.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | NAD | FAD |
|---|---|---|
| Full form | NAD is Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. | FAD is Flavin adenine dinucleotide. |
| Definition | NAD is a coenzyme that can be found in living cells. | FAD is a redox cofactor involved in many metabolic and complex reactions. |
| Production | It is produced during glycolysis and the Krebs cycle. | It is only produced during the Krebs cycle. |
| Hydrogen | It accepts only one9 hydrogen atom. | It can accept two hydrogen atoms. |
| Electron Transfer | It transfers its electron to Cytochrome Complex 1 and gives 3 ATP. | It transfers its electron to Cytochrome Complex 2 and gives 2 ATP. |
What is NAD?
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, also known as NAD, consists of two nucleotides joined together by a phosphate group.
Apart from electron transfer, it also helps in the cellular process, such as acting as a catalyst or reagent of enzymes or adding and subtracting chemical groups from the protein itself. NAD and its enzymes are so important that it becomes very vital in drug discovery.
It has a molar mass of 663.43g/molecule. Its melting point is 60 °C (320 °F; 433 K). It looks like a white powder whether it is in any state and is hygroscopic and water-soluble(highly) in nature.
What is FAD?
Flavin adenine dinucleotide, also known by the name FAD is very vital in the field of biochemistry. It is a redox-active coenzyme that is associated with different types of protein. It has four states in which it can exist: quinone, semiquinone,flavin-N(5)-oxide, and hydroquinone.
Like NAD, FAD also has two parts: the adenine nucleotide and the flavin mononucleotide (FMN) bonded together by phosphate groups. FAD can be reduced to form FADH2 by accepting two hydrogens and two electrons.
In different states, FAD has different colors. Like in a super oxidized state, it turns yellow-orange. In the fully oxidized state, it is yellow. In the half-reduced form, it is either red or blue-like pH; if reduced fully, it becomes colorless.
Main Differences Between NAD and FAD
- NAD accepts only one hydrogen atom. FAD can accept two hydrogen atoms.
- NAD transfers its electron to Cytochrome Complex 1, giving 3 ATP for each NADH produced. FAD transfers its electron to Cytochrome Complex 2, giving 2 ATP for each FDH2 produced.
- https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/bi002061f
- https://academic.oup.com/nar/article-abstract/31/3/e8/1130007
Last Updated : 11 June, 2023

Piyush Yadav has spent the past 25 years working as a physicist in the local community. He is a physicist passionate about making science more accessible to our readers. He holds a BSc in Natural Sciences and Post Graduate Diploma in Environmental Science. You can read more about him on his bio page.

The article’s emphasis on the importance of NAD and FAD in cellular processes was enlightening.
It’s impressive to see such detailed analysis. It’s a valuable resource for those interested in biochemistry.
Agreed. It highlights the significance of these coenzymes in biological systems.
This article’s scientific rigor is exemplary. It’s a valuable resource for anyone interested in biochemistry.
Absolutely. The analytical approach makes it a compelling read.
The depth of scientific detail is what makes this article stand out. A great contribution to the field of biochemistry.
The scientific depth of the article is truly commendable. A well-structured and informative read.
A solid delve into the intricacies of coenzymes. This article is a gem for biochemistry enthusiasts.
The comparison table was very useful. It helped me understand the differences between NAD and FAD clearly.
This is a really informative article. I appreciate the detailed explanation of the main differences between NAD and FAD!
I completely agree. The information presented here is top-notch and well-researched.
Impressive analysis from a biochemistry perspective. Kudos to the author for such an insightful piece.
I appreciated the detailed references provided. It shows the thorough research behind the content.
The references definitely add credibility to the article. A well-researched piece indeed.
The explanation of the various states of FAD was particularly interesting and added depth to the topic.
The article’s comprehensive overview of FAD left a lasting impression on me.
Absolutely. The in-depth analysis of FAD’s different states was enlightening.
I found the section about the molar mass and melting point of NAD quite interesting. It added a scientific depth to the discussion.
Absolutely, the scientific details made the article more engaging.
The article’s scientific focus is commendable. It’s a great read for intellectual minds.