Nephrons are basic structural and functional units of the kidney. A human kidney’s number of nephrons ranges from 8 lacks to 1 crore.
Nephrons can be distinguished into Cortical and Juxtamedullary based on their location of the Malpighian corpuscles and the length of the loop of Henle.
Key Takeaways
- Cortical nephrons are located primarily in the renal cortex and makeup about 85% of nephrons in the human kidney.
- Juxtamedullary nephrons have their renal corpuscles close to the medulla, and their loops of Henle extend deep into the inner medulla, playing a vital role in urine concentration.
- Both nephrons are essential for kidney function and filtration, but they differ in their location within the kidney and their specific roles in urine production.
Cortical vs Juxtamedullary Nephrons
The difference between Cortical and Juxtamedullary nephrons is that cortical nephrons. Malpighian corpuscles are located in the outer cortex. In contrast, Juxtamedullary nephron Malpighian corpuscles are located under the base of pyramids.
Also, in cortical nephrons, the loop of Henle is short, while in Juxtamedullary nephrons, the loop of Henle is long. About 85% of the human kidney is made up of cortical nephrons, and about 15% is made up of Juxtamedullary nephrons.
The main function of cortical nephrons is to carry out the human body’s major regulatory and excretory functions. The main function of the Juxtamedullary nephrons is to concentrate or dilute urine.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Cortical Nephrons | Juxtamedullary Nephrons |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cortical nephrons are microscopic structural and functional kidney units with a short loop of Henle. | Juxtamedullary nephrons are microscopic structural and functional kidney units with a long loop of Henle. |
| Loop of Henle | They have a short loop of Henle and only penetrate the outer renal medulla. | They have a long Henle loop extending deep into the renal medulla. |
| Malpighian Corpuscles | Their Malpighian corpuscles are located in the outer parts of the renal cortex. | Their Malpighian corpuscles are located close to the renal medulla. |
| Occurrence | Cortical nephrons are about 85% of all the nephrons in the human kidney. | Juxtamedullary nephrons are about 15% out of all the nephrons in the human kidney. |
| Function | These nephrons carry out a central part of the regulatory and excretory functions in the human body. | These nephrons concentrate or dilute the urine in the human body. |
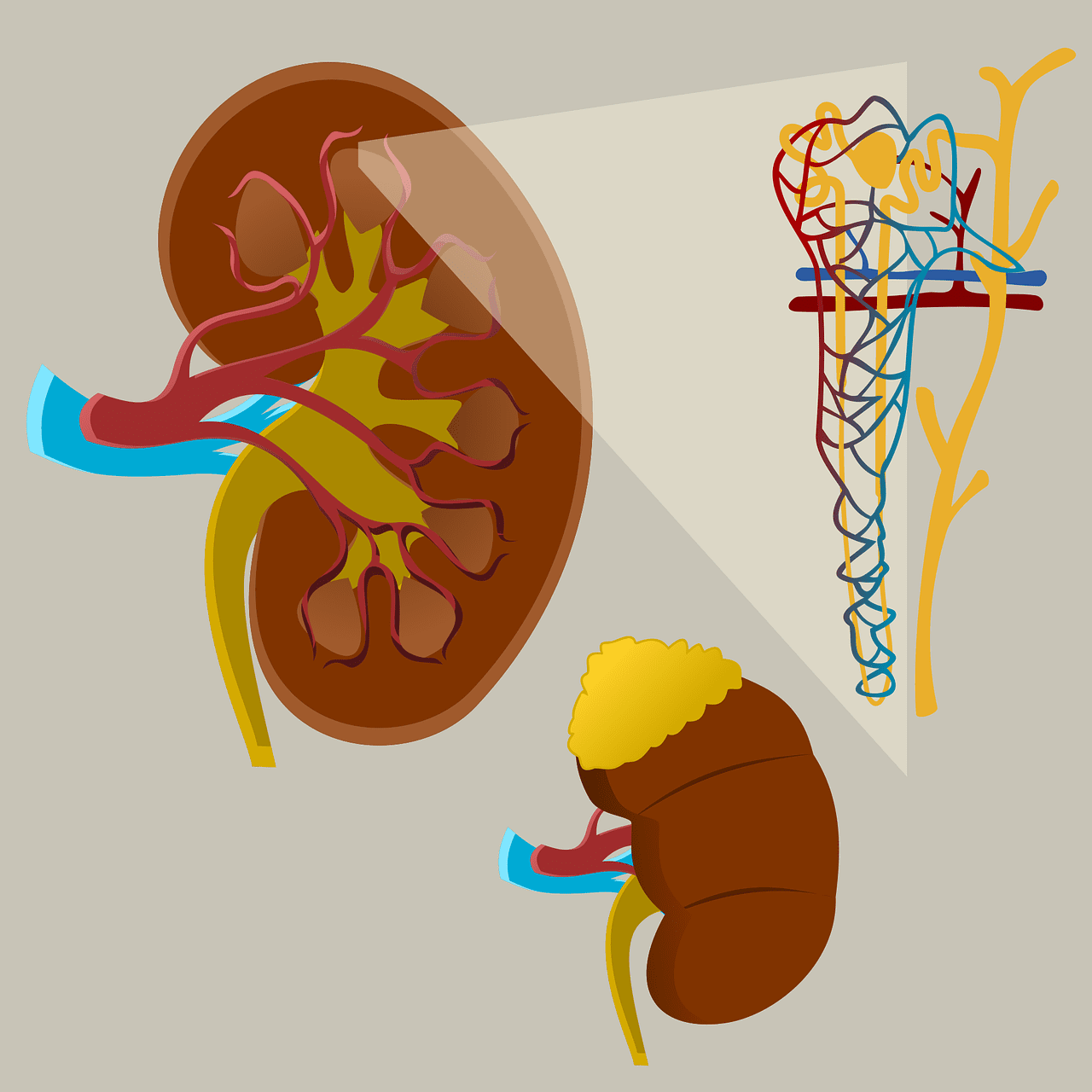
What is Cortical Nephrons?
Cortical nephrons are microscopic structural and functional kidney units with a short loop of Henle that only penetrates the outer renal medulla. Their Malpighian corpuscles are located in the outer parts of the renal cortex.
Cortical nephrons occur in all vertebrates. They carry out the central part of the regulatory and excretory functions in the human body.
A small network of capillaries, glomerulus, is located at the beginning of every cortical nephron in the outer renal cortex. The glomerulus filters the blood from the afferent arteriole of the renal arterial circulation.
Water, ions, amino acids, glucose, and other small molecules are filtered during filtration. Red blood cells, white blood cells, large proteins and platelets remain inside the glomerulus.
The others flow to the renal calyx as urine. A vascular network around Henle’s loop called the Vasa recta reabsorbs most of the water, ions, amino acids and glucose.
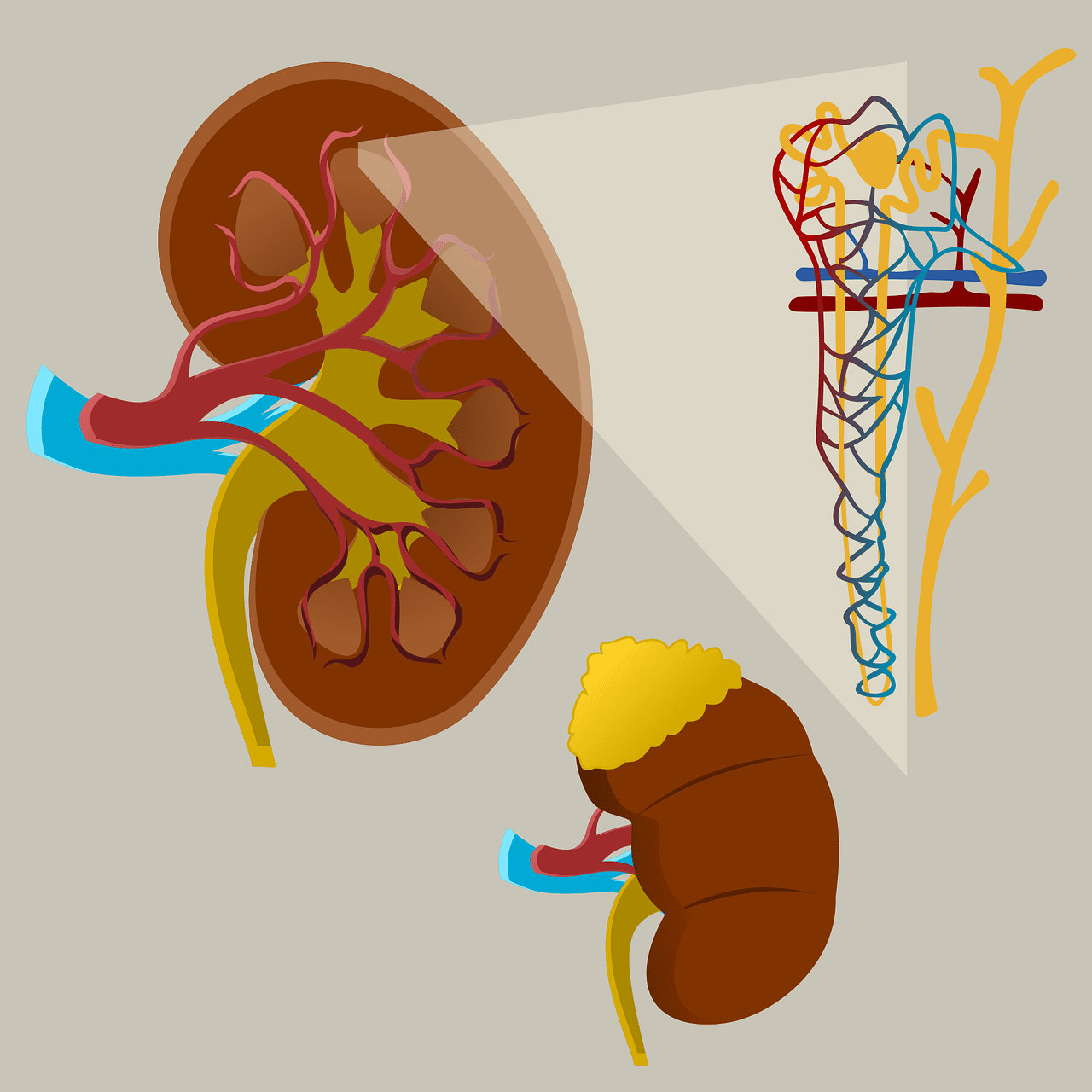
What is Juxtamedullary Nephrons?
Juxtamedullary nephrons are microscopic structural and functional kidney units with a long loop of Henle that extends deep into the renal medulla. Their Malpighian corpuscles are located close to the renal medulla.
Juxtamedullary nephrons only occur in birds and mammals. They make up 15% of all nephrons in the human kidney.
A large glomerulus is situated at the very beginning of each Juxtamedullary nephron.
The filtration rate of these nephrons is directly proportional to the size of their glomerulus. The bigger the size of the glomerulus, more is the rate of filtration.
A large Vasa recta network surrounds the long loop of Henle in these nephrons.
The generation of a hyperosmolar gradient leads to the production of concentrated urine. The main function of the Juxtamedullary nephrons is to concentrate or dilute urine in the body.
The urine concentration depends on the quantity of water the Vasa recta absorbs. If more water is absorbed, the urine will be more concentrated.
If less water is absorbed, the urine will be more diluted.
Main Differences Between Cortical and Juxtamedullary Nephrons
- Cortical nephrons are microscopic structural and functional kidney units with a short loop of Henle. In contrast, Juxtamedullary nephrons are microscopic structural and functional kidney units with a long loop of Henle.
- Cortical nephrons have a short loop of Henle and only penetrate the outer renal medulla. In contrast, Juxtamedullary nephrons have a long loop of Henle extending deep into the renal medulla.
- The cortical nephron’s Malpighian corpuscles are located in the outer parts of the renal cortex, while the Juxtamedullary nephron’s Malpighian corpuscles are located close to the renal medulla.
- Cortical nephrons are about 85% of all nephrons, whereas Juxtamedullary nephrons are about 15% in the human kidney.
- Cortical nephrons carry out the most significant parts of the regulatory and excretory functions, while Juxtamedullary nephrons concentrate or dilute the urine in the human body.
- In the Cortical nephron, the size of the glomerulus and Vasa recta are small, whereas, in the Juxtamedullary nephron, the size of the glomerulus and Vasa recta are large.
- https://journals.physiology.org/doi/abs/10.1152/ajprenal.1984.246.3.f349
- https://www.jci.org/articles/view/107663/files/pdf

The explanation of the differences between cortical and juxtamedullary nephrons is extremely clear and factual. It provides a great understanding of their respective functions.
Absolutely, I appreciate the thoroughness of the content on such a complex topic. This article was helpful in allowing me to comprehend the details.
I was amazed by the level of detail provided in this article. It truly gives an in-depth look into the functionality of nephrons in the human kidney.
It’s impressive to learn about the incredible complexity of nephrons. This article has offered valuable insight into their functioning.
This article truly offers valuable insight into the complexities of nephrons. The description of the differences was clear and comprehensive.
The in-depth exploration of nephrons in this article makes for a highly informative read. Very well-presented information.
This article takes a complex topic and breaks it down in a clear and structured manner, offering valuable insights that are easy to understand.
The article offers an incredibly detailed analysis of the differences between cortical and juxtamedullary nephrons. It’s a very informative and engaging read all around.
I appreciate the detailed information provided in the article, it made for a very engaging read.
The comprehensive and well-organized content presents a thorough examination of nephrons, making it easier to comprehend their intricate functioning.
This article used a clear and organized style to articulate the complex subject matter of nephrons. The comparison table was particularly beneficial in illustrating the differences
The in-depth analysis of cortical and juxtamedullary nephrons provides valuable insight into their roles within the kidney. The comparisons have made it easy to understand the differences.
The content is rich, well-organized, and incredibly informative. It breaks down the differences between cortical and juxtamedullary nephrons in a very clear and concise manner.
I found it extremely useful for understanding such complex nephron details in an understandable format
The article really simplifies the complexities of nephrons, making the understanding of their functions much more accessible.
The article delves into a detailed comparison of cortical and juxtamedullary nephrons. It is an excellent resource for understanding the complexities of kidney function.
The content’s well-written and comprehensive nature brings significant insight into the differentiation between cortical and juxtamedullary nephrons. Both of their roles are well-described as well.
It’s an excellent reference for anyone wanting to delve into the topic of nephrons. The details are presented in a clear and engaging manner.
The article is truly a great source for understanding the concept of nephrons. The content is rich and well-structured.
It’s astonishing to learn that the human kidney can contain such a high number of nephrons, from 8 lacks to 1 crore. This article has provided an enlightening insight into nephrons.
Absolutely, it’s fascinating to discover the scope of nephrons in kidney function. I’m glad it was explained so thoroughly in this article.
The detailed comparison table provided a comprehensive account of the differences between cortical and juxtamedullary nephrons, which was very helpful.
This is a very informative and in-depth article about the different types of nephrons in the human kidney. It uses a very clear and organized structure to present the information.
I completely agree, the level of detail is impressive and makes it easy to understand such complex topics