Hepatitis and Cirrhosis are diseases that affect the liver and its functions.
So some of the symptoms of these diseases are very similar, like itching, blood in vomiting, fatigue, abnormal muscle moments, amnesia, swelling in legs and discomfort in the sleeping cycle, etc.
Though many differences should be noted to differentiate between the two.
Key Takeaways
- Hepatitis is a liver inflammation caused by a virus, excessive alcohol consumption, or other factors.
- Cirrhosis is a late-stage liver disease that results from long-term liver damage, such as hepatitis or alcohol abuse.
- Hepatitis can be treated with medication, while cirrhosis may require a liver transplant.
Hepatitis vs Cirrhosis
Hepatitis refers to inflammation of the liver caused by a viral infection but may also be due to toxins, autoimmune diseases, or heavy alcohol use. Cirrhosis is a late stage of scarring (fibrosis) of the liver caused by many forms of liver diseases and conditions, such as hepatitis and chronic alcoholism.
Hepatitis is a viral infection that affects the liver. It causes inflammation of the liver, which leads to damage of the liver tissue that causes swelling. Hepatitis can be an acute or chronic infection.
There are different types of hepatitis, the main of them are Hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E.
It is considered that Cirrhosis happens because of the regular damage to the liver by chronic hepatitis infection. The proliferation of the liver is caused by cirrhosis by an increase in the production of connective tissues in the liver.
And so it distorts or blocks the blood flow in the liver. Chronic hepatitis can lead to cirrhosis.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Hepatitis | Cirrhosis |
|---|---|---|
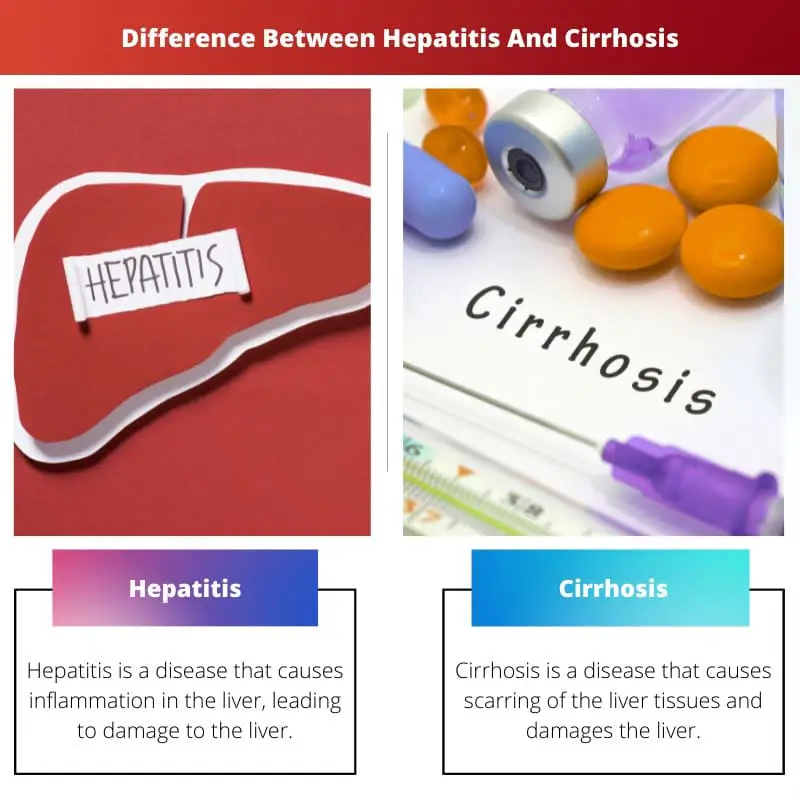
| Definition | Hepatitis is a disease that causes inflammation in the liver, leading to damage to the liver. | Cirrhosis is a disease that causes scarring of the liver tissues and damages the liver. |
| Cause | Mostly, it is caused because of the infection. | Chronic hepatitis, alcohol consumption are the main causes. |
| Symptoms | Fatigue, fever, dark urine, abdominal pain, loss of appetite, etc. | Loss of appetite, fever, fatigue, Itchy Skin, memory loss, swelling in legs, weight loss, etc. |
| Complications | Liver failure, Liver cancer, etc. | Portal Hypertension, Malnutrition, Liver failure, Hypersplenism, etc. |
| Treatment | Anti-viral medications, Anti-viral drug therapies. | Anti-biotic, Anti-viral medication. |
What is Hepatitis?
Hepatitis is a disease that causes inflammation in the liver, which leads to damage to the liver tissue. Hepatitis can lead to liver failure as well.
It is commonly the result of a viral infection, though there are other possible causes of hepatitis, like alcohol consumption.
Hepatitis can be acute or chronic, i.e. it can be short-term or long-term. There are many types of hepatitis. Hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E are the main types of Hepatitis, and each of them can be caused by different types of viral infection.
Hepatitis A is caused because of hepatitis A virus infection. Hepatitis B can happen due to the hepatitis B virus (HBV). Hepatitis C virus or bloodborne viral infections causes Hepatitis C.
Hepatitis D is caused because of hepatitis D virus (HDV) or in conjunction with hepatitis B infection. And Hepatitis E occurs due to the hepatitis E virus (HEV), caused by poor sanitation and contaminated water.
Another type of hepatitis is autoimmune hepatitis, in which the body makes antibodies against the liver tissues of the body. This can occur because of side effects or secondary results of medications or drugs.
Exposure to toxins and chemicals can also be a reason. Blood tests, Imaging tests, Liver biopsies, etc., are used to diagnose the disease.
What is Cirrhosis?
Cirrhosis is a disease that causes damage to the liver. It is a late-stage disease. In cirrhosis, the healthy liver tissues are replaced with scar tissues, leading to liver damage.
Scar tissue keeps the liver from working properly and causes cell death and inflammation. The scarring of the liver leads to blockage of the flow of blood through the liver.
This leads to liver dysfunction, and the liver cannot work properly. Its ability to process nutrients, proteins, hormones, drugs, natural toxins, and other substances is compromised.
Cirrhosis can occur because of chronic hepatitis, alcohol consumption, diabetes, obesity, unprotected sex, or taking drugs through shared needles, or it can be genetic.
Some symptoms of cirrhosis are abdominal pain, diarrhoea, fever, nausea, itchy skin, weight loss, etc. There are two stages of cirrhosis: Compensated cirrhosis, Decompensated cirrhosis.
Compensated cirrhosis means the symptoms of cirrhosis are not yet visible in the patient though he has cirrhosis. And Decompensated cirrhosis means the cirrhosis is worsened, and the symptoms are noticeable now.
Cirrhosis is fatal, and it has complications like liver failure, portal hypertension, etc. Until recently, it was believed that Cirrhosis cannot be reversed and the damage is done permanently.
It can be stopped at a limit but cannot be reversed however, recent studies have taken some points into consideration and showed that it can be reversed.
CT scans, MRI, blood tests, Ultrasounds, etc., are used to diagnose cirrhosis.
Main Differences Between Hepatitis And Cirrhosis
- Hepatitis occurs due to a viral infection. Cirrhosis occurs either because of chronic hepatitis, alcohol consumption, or it can be genetic.
- Hepatitis can be acute or chronic. Cirrhosis is chronic.
- Hepatitis is reversible. Cirrhosis was irreversible until recently, and research has come out with ways to reverse it.
- Hepatitis has types or forms like Hepatitis A, B, etc. Cirrhosis has no type.
- The major complications of hepatitis are ALT, Relapsing hepatitis, etc. The major complications of Cirrhosis are haemorrhaging, portal hypertension, etc.
- https://aasldpubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/hep.1840060302
- https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/255016/9789?sequence=1
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0140673608603839

This is a well-explained post.
I completely agree. It provides clear insights into the diseases.
The content was a bit too dense to read.
I found the article to be a comprehensive guide on the topic.
The article should have included more scientific studies as references to solidify the information presented.
I think the information is adequate without the need for further extensive studies.
The content is quite informative.
The author’s approach to simplifying complex medical concepts was commendable.