Symbiosis is the most crucial biological process required in the ecosystem. It is the prime process that instigates evolution.
Lactobacillus and Humans are the best examples of a symbiotic relationship. Our human body has thousands of bacteria without which we cannot survive.
The organisms that undergo the process of symbiosis are called Symbionts. If the symbionts are living on the surface of the other organism, it is called ectosymbiosis.
When talking about Symbiosis, there are three major types of Symbiotic Processes. Mutualism, Commensalism and Parasitism.
Mutualism and Commensalism shall sound similar in their interaction, but there are differences between the two.
Key Takeaways
- Mutualism is a symbiotic relationship between two organisms in which both species benefit from the interaction, such as bees pollinating flowers while gathering nectar.
- Commensalism is a symbiotic relationship where one organism benefits without affecting the other organism, such as barnacles attaching to a whale for transportation without harming the whale.
- The key difference between mutualism and commensalism is the outcome for each organism involved; in mutualism, both organisms benefit, while in commensalism, one organism benefits without affecting the other.
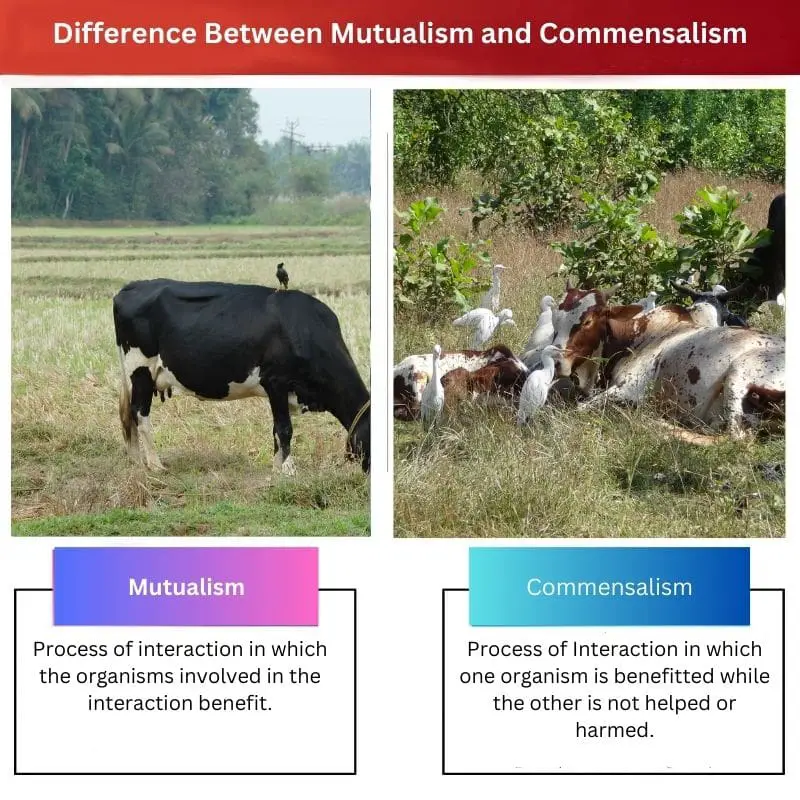
Mutualism vs Commensalism
Mutualism is a form of symbiotic relationship in which all the species involved will benefit from the interactions, and it is a common type of ecological interaction. Commensalism is a process of long-term biological interaction in which some species benefit and others are getting harmed.

Comparison Table
| Parameter of Comparison | Mutualism | Commensalism |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning/ Definition | Process of interaction in which the organisms involved in the interaction benefit. | Process of Interaction in which one organism is benefitted while the other is not helped or harmed. |
| Benefit | There is a mutual benefit among all the organisms involved. | Only one organism is benefitted from this interaction. |
| Type of relationship | Obligatory Relationship | Non-Obligatory relationship |
| Major Types | Nutritional, Defence, Transport and Shelter | Transport, Shelter, Food |
| Examples | The interaction between bees and the flower, Bacteria and Human Beings | Remora and Shark, Aspergillus and Humans |
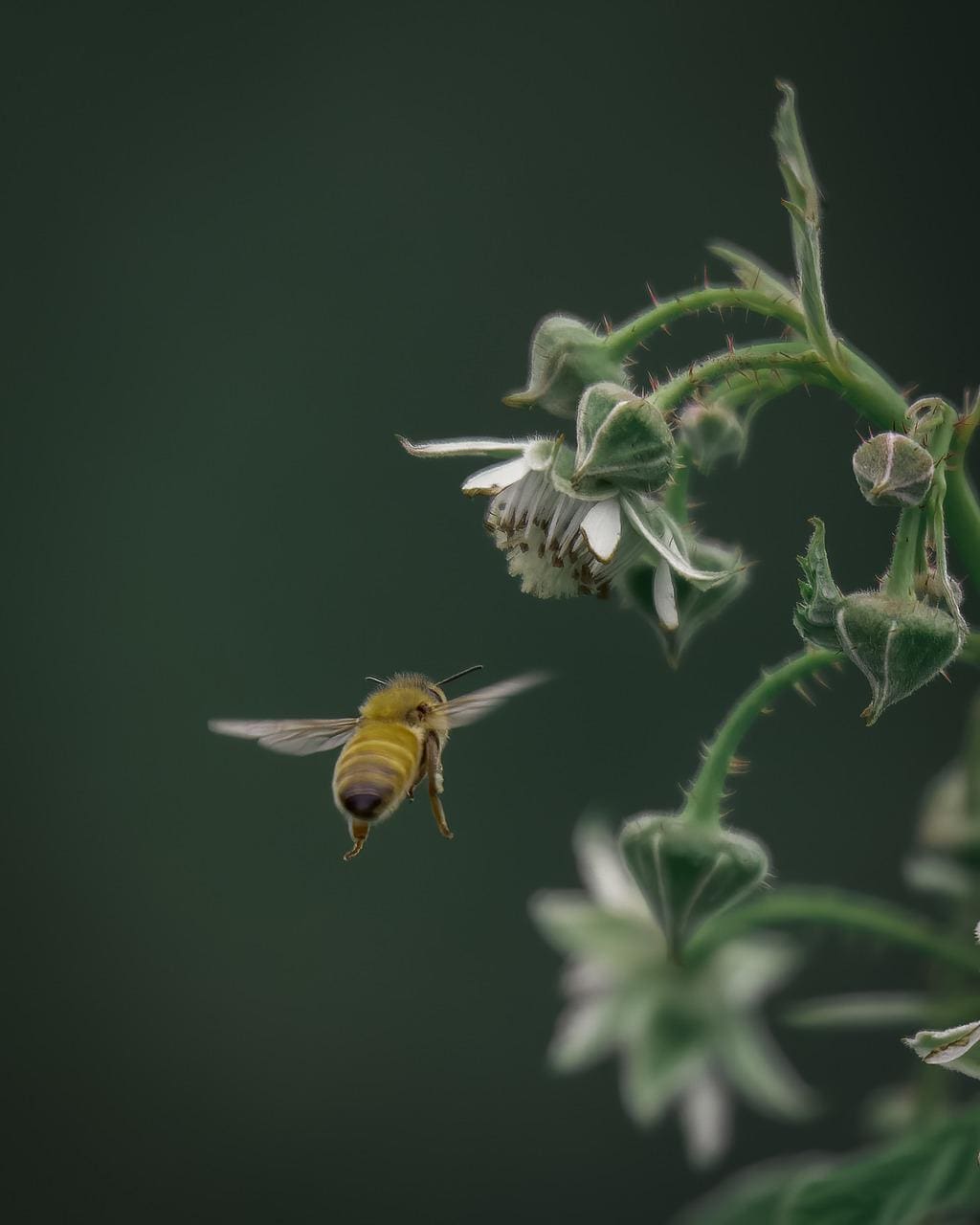
What is Mutualism?
Mutualism is a symbiotic process where two or more organisms interact closely and benefit mutually. It is indeed considered a positive interaction between organisms.
Mutualism exists for many reasons; they may be categorized as
- Transportation Mutualism
- Nutritional Mutualism
- Shelter Mutualism
- Defence Mutualism
In all the above processes, whichever organisms interact with will be benefitted. The relationship is considered Obligatory, and both organisms are required for survival.
This type of ecological interaction is considered standard. Examples can be cited as
- Animals pollinating flowering plants
- Humans and Bacteria
Mutualism is also considered the most critical symbiotic process for the terrestrial ecosystem. It is observed 48% of plants rely on Fungi, and this happens through Mutualism only.
At the same time, the animal seed-dispersing mutualistic process accounts for up to 90% of the evolution of the world.
Mutualism is categorized based on the interactions the organisms have between them.
- Service and Resource Relationship: This is by far the typical mutualistic relationship.
- Service and Service Relationship: This is rare to find where organisms rely on each other’s services.
Mutualism helps in the survival of organisms as well as their growth. It is one of the critical processes to induce evolution.

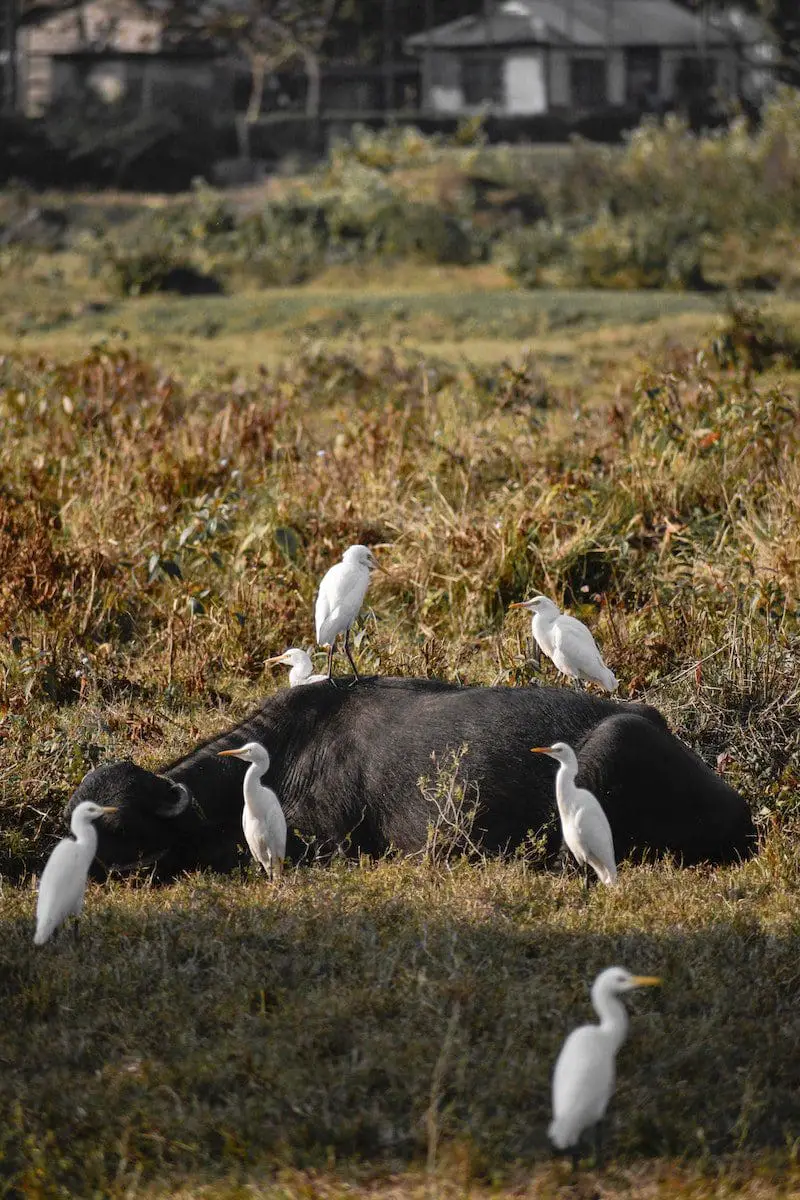
What is Commensalism?
Commensalism is a symbiotic relationship where two or more organisms are involved. Commensalism is a process where one organism is benefitted while the other is unaffected.
That means to say, the organism is neither harmed nor benefitted. Commensalism is expected due to a few factors.
- Transport Commensalism
- Shelter Commensalism
- Food Commensalism
- Defence Commensalism
The organisms that involve in such interactions are called Commensals. It is observed that Commensalism takes place between a smaller commensal and a larger one.
As per the process, the host, the bigger commensal, remains unaffected, while the more minor commensal benefits in one way or another.
Like Mutualism, Commensalism also has different types
- Inquilinism: An interaction where the smaller commensal finds a permanent shelter in the host
- Metabiosis is an interaction where the smaller commensal uses the dead animal as a host to survive.
- Phoresy is the interaction where a small commensal utilizes the larger one for transportation.
The experts always feel that explaining commensalism is difficult as the process of one organism not being affected is practically not actual. The host also undergoes morphological adaptation during the interaction.

Main Differences Between Mutualism and Commensalism
- The main difference between Mutualism and Commensalism is the process of interaction. Mutualism is a symbiotic process where both symbionts are benefitted. At the same time, commensalism is an interactive process where one organism ultimately helps while the other is unaffected.
- The interaction process for Mutualism is considered ‘Obligatory’ for the organisms’ mutual obligation, while Commensalism is called ‘Non-Obligatory’ interaction.
- Mutualism establishes benefits for all the organisms involved, while commensalism does not exhibit such characteristics. It is only one organism that is benefitted.
- Nutritional Benefits are gained in the Mutualism process, while Commensalism is more for a shelter and transport-based interaction.
- A complete morphological adaptation of the organisms might happen or give rise to a whole new organism or a species through Mutualism. In contrast, Commensalism does not give rise to any new species, and their morphological adaptation is limited.
- https://www.srs.fs.usda.gov/pubs/ja/ja_hofstetter002.pdf
- https://www.journals.uchicago.edu/doi/abs/10.1086/283384
This article has been written by: Supriya Kandekar

I think there’s a wealth of knowledge in this article, and the explanations are fantastic.
Absolutely, it’s a treasure trove of information.
I enjoyed reading this article, I appreciate the clear distinction between Mutualism and Commensalism.
I agree, the differentiation is very clear.
I never understood the difference before, but this article made it very clear.
This post is very informative, but the tone is a bit dry. Adding real-life examples or case studies would make it more engaging.
I believe a more engaging tone would bring this post to life.
I get what you mean, more practical examples would make it easier to relate to.
This article is too wordy, it could be a little more concise and to the point.
I agree with you, the information is great but it could be more succinct.
While your information is accurate, I find the lack of personality in the writing style to be dull.
I understand your point, but this writing style is the case for scholarly articles.
I don’t mind the writing style, I’m more interested in the content.
The post is very enlightening, but a touch of humor would make it even better!
I agree, a bit of humor would definitely add an interesting twist to the content.
I particularly like the comprehensive information you have provided about Mutualism and Commensalism, it is indeed enlightening.
I completely agree with you, it’s a great explanation.
Appreciate the depth of information provided here, really insightful.
It’s detailed, but not overwhelming. A great balance.
The comparison table provides a clear summary of the differences between the two, very well done.
I agree, the table simplifies the information really well.
Great way to convey the information effectively.
While I appreciate the detail, it would be great to see more opinion along with the facts.
I understand where you’re coming from, but objectivity is crucial in this type of content.