Irrespective of the fact that Myeloid and Lymphoid both have the same suffix “–oid,” they are different from each other. Both terms refer to the components of a certain organ or structure found in the human body.
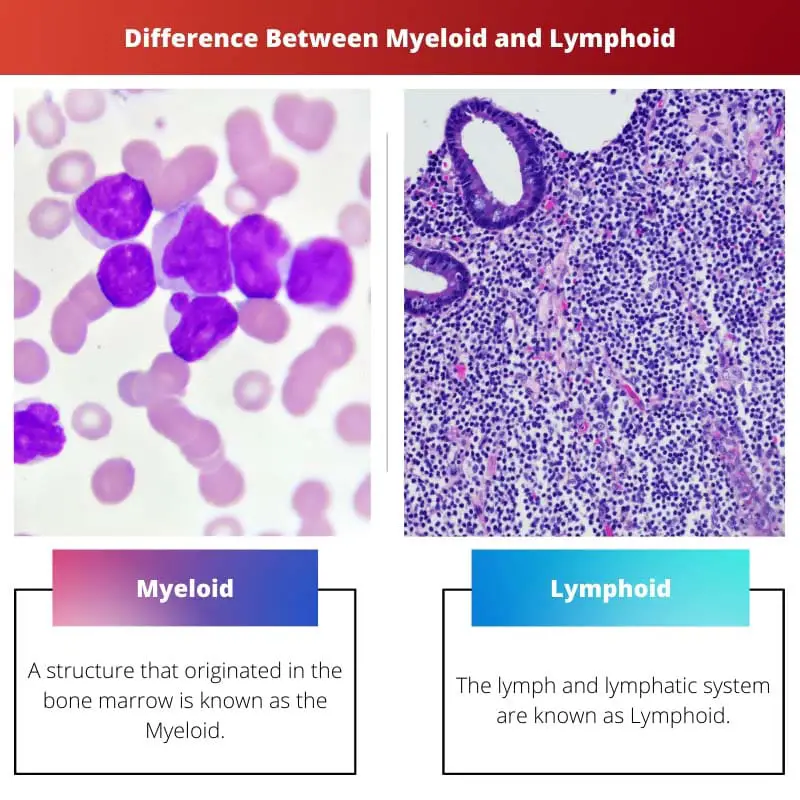
Myeloid refers to the structure of bone marrow, and lymphoid refers to the lymph or lymphatic system.
Key Takeaways
- Myeloid cells are produced in the bone marrow and include red blood cells, platelets, and various types of white blood cells, while Lymphoid cells are produced in the lymphoid organs and include T cells, B cells, and natural killer cells.
- Myeloid cells are involved in blood clotting, oxygen transport, and immune response, while Lymphoid cells are involved in the adaptive immune system.
- Myeloid cells are found in the blood and tissues, while Lymphoid cells are primarily found in the lymph nodes, spleen, and thymus.
Myeloid vs Lymphoid
Myeloid cells include red blood cells, platelets, and various types of white blood cells, such as neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils, monocytes, and macrophages. Lymphoid cells include B, T, and natural killer cells, which are involved in the immune response to infections and cancer.
Myeloid is a term used to define the structure that originates in the bone marrow of a human body and refers to an illness related to blood or occurring in the bone marrow. When there is a severe lack of red blood cells in the body, it leads to cancer in the bone marrow.
Lymphoid is a term used to define the composition of a human body known as lymph or lymphatic system, and the term is also used while describing a cancerous disease in the lymphatic system known as lymphoid leukaemia.
The lymphatic system of the human body is mainly responsible for its immune protection.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Myeloid | Lymphoid |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A structure that originated in the bone marrow is known as the Myeloid. | The lymph and lymphatic system are known as Lymphoid. |
| Other definition | Myeloid is also used to define the illness occurring in the bone marrow. | Lymphoid is also used to define the illness occurring in the lymphatic system. |
| Disease development | It can occur in both RBC and WBC. | It occurs in the WBC only. |
| Subtypes | Myelodysplastic syndrome | Hairy cell leukemia |
| Types of malignancies | AML and CML. | ALL and CLL. |
What is Myeloid?
The myeloid term is used to describe the bone marrow structure in a human body, and the bone marrow contains myeloid cells, which are multipotent type stem cells.
The myeloid cells produce many types of blood cells in the body, namely red blood cells (RBC), granulocytes like monocytes, neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, and platelets.
There are two types of malignancies that occur in the bone marrow known as acute myelogenous/myeloid leukaemia (AML) and chronic myelogenous/myeloid leukaemia (CML).
These two types of cancer happen due to the rapid growth of abnormal cells. Acute myelogenous/myeloid leukaemia (AML) is a fast-growing form of blood or bone marrow cancer.
Chronic myelogenous/myeloid leukaemia (CML) occurs in the blood-forming cells of bone marrow, and later with the span of time, it spreads to the bloodstream therefore, as the blood reaches other parts of the body, the disease spreads in the whole body.
There is another type of disease relating to myeloid known as Myelodysplastic Syndrome (MDS), in which there is an abnormal behaviour shown by the bone marrow as it produces a fewer amount of functioning red blood cells (RBC), white blood cells (WBC), or platelets in the body.
The cells in the blood and bone marrow seem to be abnormal when diagnosed.

What is Lymphoid?
Lymphoid, which describes the lymph or lymphatic system of the body, contains lymphoid cells, which are multipotent, hematopoietic progenitor cells.
The lymphoid cells are mainly responsible for producing T and B lymphocytes along with natural killer cells. T lymphocytes play a major role in boosting immunity.
B lymphocytes produce antibodies which play a major role in humoral immunity. Natural killer cells help to respond against virally infected cells.
There are two types of malignancies that occur in the lymphoid cells known as acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL) and chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL). These two types of cancer happen due to the production of immature lymphoblasts in large amounts.
In acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL), the healthy cells which produce functioning lymphocytes are replaced rapidly, and thus, the cells remain immature.
These immature cells then flow in the bloodstream to different body parts, where the cells divide and grow, which results in various symptoms.
Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL) is a slow-growing cancer disease that occurs when abnormal lymphocyte growth obstructs normal cells, making it difficult to fight any infection.
The subtype of CLL, also known as hairy cell leukaemia (HCL), occurs when there is a large production of B cells.
Main Differences Between Myeloid and Lymphoid
- Myeloid refers to the structure that originated or is related to the bone marrow, whereas lymphoid refers to the body’s lymph or lymphatic system.
- The term myeloid is also used to refer to a cancerous illness that is related to or occurs in the bone marrow, whereas on the other hand, the term lymphoid is also used to refer to an illness relating to or which occurs in the lymphatic system.
- The myeloid disease develops and attacks both the white blood cells (WBC) as well as the red blood cells (RBC). On the other hand, the lymphoid disease known as lymphoid leukaemia attacks and develops in the white blood cells (WBC) only.
- Myelodysplastic syndrome is the subtype of myeloid-related disease in which the bone marrow produces a very less amount of functioning RBC, WBC, or platelets, and on the other hand, hairy cell leukaemia is the subtype of chronic lymphatic leukaemia in which the bone marrow produces too many B cells.
- In myeloid, AML and CML are the main types of malignancies, whereas in lymphoid, ALL and CLL are the main types of malignancies.
- https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/nejm199909303411407
- https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMra1406184
- https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJM199904293401706
- https://ashpublications.org/blood/article-abstract/107/9/3481/133476

The detailed explanation of different types of malignancies related to myeloid and lymphoid cells is an excellent addition to this article. It enriches the reader’s understanding.
Absolutely, the depth of information provided about these malignancies is incredibly insightful and enables a better grasp of the topic.
The comparison table provided in the article offers a comprehensive breakdown of the defining characteristics of myeloid and lymphoid cells. It’s a great reference to have.
Indeed, the clear presentation of information through the comparison table is immensely helpful for those seeking detailed insights into cellular biology.
The explanation of myeloid and lymphoid cells in this article is exceptional. It provides a clear understanding of their biological functions.
Indeed, the in-depth comparison of these cellular components offers valuable insights for anyone interested in the field of biology.
The detailed breakdown of myeloid and lymphoid cells in this article is enlightening. One can gain a better understanding of the roles they play in the body’s immune system.
I appreciate the emphasis on the crucial functions of myeloid and lymphoid cells in immune response. This article provides a valuable perspective.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of myeloid and lymphoid cells, shedding light on their structure and functions within the human body.
Agreed. The breakdown of the role each type of cell plays in the body’s immune system is incredibly enlightening.
Absolutely, this article serves as an excellent reference for understanding the significance of myeloid and lymphoid cells in the context of human health.
The article elegantly highlights the differences between myeloid and lymphoid cells, contributing to a deeper comprehension of these biological entities.
Absolutely, the article’s emphasis on the distinct functions of myeloid and lymphoid cells helps in understanding their importance in the human body.
I couldn’t agree more. The comparison of diseases and malignancies related to these cells is particularly insightful.
It’s fascinating to learn about the different diseases related to myeloid and lymphoid cells. The explanations serve as a valuable resource for understanding these conditions.
Indeed, having a comprehensive overview of these complex medical concepts is beneficial for medical professionals and students alike.
This article does a fantastic job of elucidating the key differences between myeloid and lymphoid cells, offering an invaluable resource for those interested in the subject.
Agreed. The insights provided regarding the diseases and types of cancer associated with these cells significantly contribute to the article’s comprehensiveness.
Absolutely, the article’s structure allows for a thorough understanding of myeloid and lymphoid cells, making it an excellent educational resource.
This article provides a clear comparison between myeloid and lymphoid cells. It’s important to understand the differences between these cells, especially for those in the medical field.
I agree. The level of detail in the comparison table is particularly informative.
Absolutely. The information about various malignancies in myeloid and lymphoid cells is very useful.
This article has effectively outlined the distinct characteristics of myeloid and lymphoid cells, which are essential for a comprehensive understanding of the immune system.
I agree. This article enhances our understanding of the complexities involved in the body’s immune response.
Absolutely, the discussion on the development of diseases related to myeloid and lymphoid cells is particularly intriguing.