The foundation for inorganic and organic chemistry is organic and inorganic compounds. Organic chemists research, evaluate and observe the reactions of organic compounds.
Several other compounds, like salts, metals, and minerals, are examined by inorganic chemists.
Key Takeaways
- Organic compounds contain carbon-hydrogen (C-H) bonds, derived from living organisms or their by-products, and are the basis of all known life forms.
- Inorganic compounds do not contain carbon-hydrogen bonds, encompassing many substances, including minerals, metals, and salts, not associated with living organisms.
- The main difference between organic and inorganic compounds is the presence of carbon-hydrogen bonds, a key characteristic of organic compounds that distinguishes them from inorganic substances.
Organic vs Inorganic Compounds
The difference between Organic and Inorganic Compounds is that organic compounds have the element carbon, while this molecule is absent in most inorganic compounds.
However, inorganic substances containing carbon cannot be classified as organic because the amount of carbon is negligible! Organic compounds comprise carbon atoms bound to hydrogen atoms to create the C-H bonds, with slight deviations.
Several organic compounds have oxygen atoms.
Comparison Table
| Parameter of Comparison | Organic | Inorganic |
|---|---|---|
| Presence of carbon atom | They are distinguished by the carbon atoms which are present in them | Inorganic substances do not comprise carbon atoms |
| Reactivity | They are considered to be more reactive and extremely flammable | They are naturally not volatile and are also not flammable |
| Physical state | These substances occur as gases, liquids, and solids. | They solely occur as solids |
| Occurrence | Organic substances are present predominantly in most living organisms | They majorly occur in non-living organisms |
| Melting and boiling points | High melting and boiling points are among the main aspects used to characterize organic substances. | Compared to organic substances, these are characterized by low boiling and melting points. |
What are Organic Compounds?
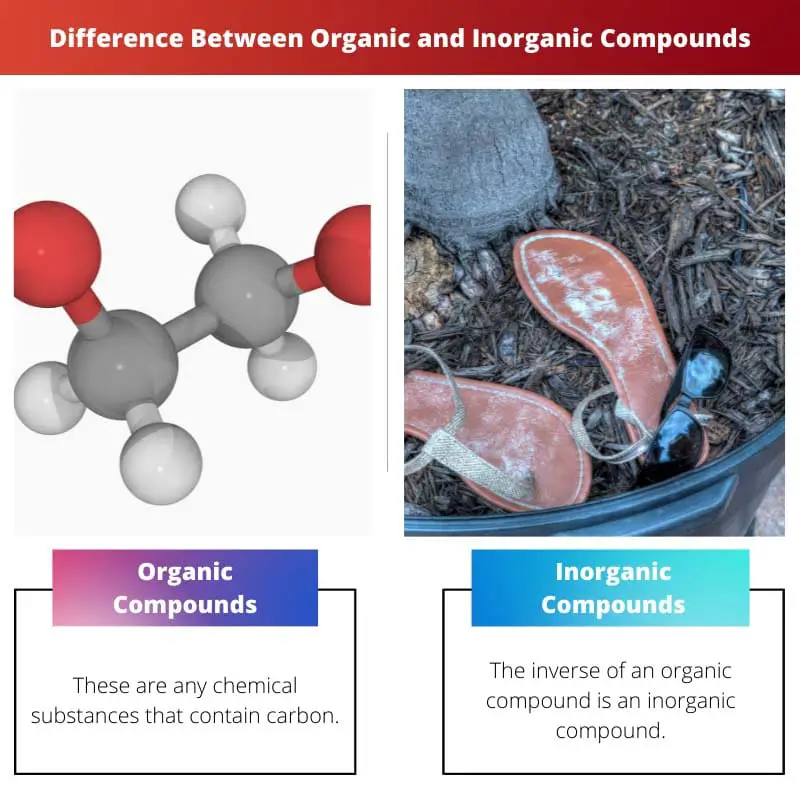
These are any chemical substances that contain carbon. Numerous organic substances are identified because of the capacity of the carbon to catenate (form chains of certain carbon atoms).
The study referred to as organic chemistry includes the evaluation of the structures and reactions of organic compounds.
While organic compounds make up just a tiny percentage of the Earth’s surface, they are of essential significance because organic compounds are the source of all known life.
Living organisms integrate inorganic carbon compounds into organic compounds through a channel of mechanisms (the carbon cycle), starting with the processing of carbon dioxide and supply of hydrogens such as water into simple sugars and other organic molecules, utilizing light (photosynthesis) or other energy sources.
Do all Organic compounds come from life?
You need to be aware that not all organic substances come from life. Many organic compounds are created inside living organisms, but molecules can be generated through other processes.
For instance, organic compounds discovered on Mars or within a nebula aren’t indicators of alien existence. Solar radiation may provide the energy required to convert inorganic compounds into organic matter.

What are Inorganic Compounds?
Simply stated, the inverse of an organic compound is an inorganic compound. To understand more about how inorganic compounds are classified, it helps to learn what makes certain compounds organic.
An inorganic compound can be referred to as a compound not having a carbon-to-hydrogen bond, also referred to as a C-H bond. Besides, inorganic substances appear to be minerals or substances not having carbon-to-hydrogen bonds, based on geology.
Not all, but most inorganic compounds have one metal in them.
What are the Characteristics of inorganic compounds?
Although several inorganic compounds comprise any form of metal (alkali, alkaline, etc.), they tend to be capable of electrical conduction. For instance, inorganic compounds are weak conductors of electricity when they are in a solid state.
However, inorganic materials are particularly conducive to the liquid form. In this step, the electrons in inorganic compounds will move very quickly, and this electron movement is recognized as electricity.
Inorganic compounds are bound together very rigidly owing to the ionic bonding contained in them and exhibit very high melting and boiling points. Colour is another distinguishing feature of inorganic compounds.
Transition metal inorganic compounds are intensely coloured, and this is again attributed to the ‘d-block’ electrons arrangement.
The vivid and colourful colours that one sees as fireworks burst are linked to the inorganic metal that is found in the compound (an alkali or alkaline one).
Since inorganic compounds exhibit a distinctive colour when burning, this can be used to classify the metal involved. In this scenario, they are used as a ‘marker.’
Inorganic materials are commonly easily soluble in water. This is to say, when put in water, they can ‘disappear’ because they dissolve.
The capacity to form crystals is yet another surprising characteristic of inorganic compounds.
The bonding structure contained in inorganic compounds gives them the potential to produce crystals in saturated solutions.

Main Differences Between Organic and Inorganic Compounds
- Organic substances are hydrocarbons because they are produced solely from carbon and hydrogen, whereas inorganic substances are not made up of carbon.
- Carbon(II)oxide, water, and carbon(IV)oxide are the products produced when organic compounds burn. At the same time, inorganic compounds do not burn, but when they do, they produce cation oxide and a cation nitride.
- Organic substances are generated from living organisms, while non-living natural mechanisms or human experimental activities generate inorganic compounds.
- Salts are produced by inorganic compounds, while organic compounds cannot generate salts.
- Organic substances are bonded by carbon-hydrogen bonds, while ionic, covalent and metallic bonds bond inorganic substances.
- Inorganic substances are characterized by the presence of n metal atoms, while organic compounds do not contain metal atoms.
- https://ebme.marine.rutgers.edu/HistoryEarthSystems/HistEarthSystems_Fall2008/Week2/Kwok_Nature_2004.pdf
- https://academic.oup.com/carcin/article-abstract/2/4/283/2389968

The author has done a great job of outlining the features and distinctions between organic and inorganic compounds. The scientific insights presented here are truly valuable.
It’s fascinating to see the detailed comparisons between organic and inorganic compounds. The impact of these compounds on the existence and behavior of matter is truly astonishing.
The author’s thorough explanation of the reactivity and occurrence of organic and inorganic compounds is highly informative. It’s a pleasure to read an article with such clarity and depth.
The illustrations provided here give an excellent visualization of the comparisons between organic and inorganic compounds. It’s both educative and engaging.
This article provides a clear overview of the differences between organic and inorganic compounds, and how they are fundamental to the substance of life as we know it on Earth.
The detailed descriptions of the reactivity and physical states of organic and inorganic compounds are truly intriguing. This article is a commendable resource for anyone interested in chemistry.
The comparison table and detailed descriptions of the reactivity and occurrence of organic and inorganic compounds are both educative and thought-provoking. This is an excellent piece of scientific writing.
The intricate descriptions of the characteristics of inorganic compounds are quite enlightening. This article provides a comprehensive understanding of the subject matter.
The in-depth explanations of the characteristics of inorganic compounds are extremely useful for gaining knowledge about the properties of different substances. Well done!
This article effectively highlights the significance of organic compounds in life forms and how the absence of carbon-hydrogen bonds characterizes inorganic compounds. It’s informative and well-presented.