Anatomy is the most important branch of biology, which studies the parts and structure of organisms especially living beings. Anatomy is a very old science, and its origin can be dated back to the prehistoric era.
Anatomy is divided into two parts, i.e. microscopic and macroscopic. Microscopic anatomy studies tissues of various structures, also called histology, i.e. the study of cells. Polyps and Cysts come under Microscopic anatomy.
Key Takeaways
- Polyps are abnormal tissue growths projecting from a mucous membrane, while cysts are closed sac-like structures containing fluid or semi-solid material.
- Polyps are commonly found in organs like the colon, stomach, and uterus, whereas cysts can develop in various body parts, including the skin, ovaries, and kidneys.
- Polyps may become malignant, while cysts are benign and pose little risk of developing into cancer.
Polyp vs Cyst
A polyp is a small, fleshy growth that can occur on the lining of organs like the colon, uterus, or nose. Polyps can be benign or cancerous, and their symptoms and treatment depend on their location and size. A cyst is a fluid-filled sac that can form anywhere in the body. Cysts can be caused by a variety of factors, including infections, injuries, or genetic disorders.

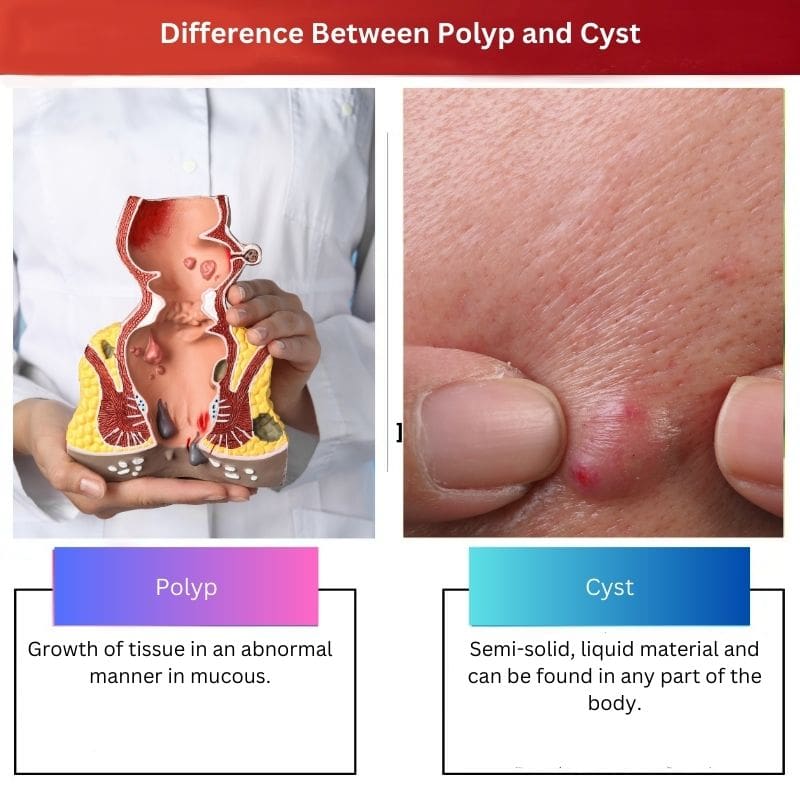
A polyp is referred to as the growth of tissue in an abnormal manner in the mucous membrane. Polyps can happen in several parts of the body, but it most commonly occurs in the colon, stomach, urinary bladder, nose, ear, sinus(es), and uterus.
Polyps can develop into tumours and can be cancerous. Polyps can also be inherited from a family, which is called Inherited Polyposis syndrome.
A cyst is like a cluster of cells that comes together to form a closed sac, just like water molecules come together to form a bubble.
The cyst can be distinguished from shells because their growth is very abnormal, and their behaviour is very distinct compared with the cells found in our body.
The cyst can be resolved on its own or by taking pills or contraceptives. But if it is not removed, then it can be removed surgically.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Polyp | Cyst |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Growth of tissue in an abnormal manner in mucous. | Semi-solid, liquid material and can be found in any part of the body. |
| Causes | Inflammation, Foreign bodies, Cysts and tumours etc. | Bacterial infections, Clogging, obstruction etc. |
| Symptoms | Chronic inflammation in the stomach, Excessive estrogen level etc. | Lump, increase in size, itchy, painful etc. |
| Treatment | Size, location, number, cancerous or non-cancerous. | Pills or surgically |
| Types | Sessile polyp, Pedunculated polyp | Acne cyst, choroid cyst, baker’s cyst, mucoid cyst etc. |
What is Polyp?
The term Polyp is very ancient and originated in the 1400s. Since then, it has been used in English. Polyp comes from the Latin word ‘polypus’, meaning nasal polyp. Earlier, the word Polyp was associated with animals, especially octopuses.
But after 1742, it came into use for human beings as well. Polyps can occur in any part of the body where the mucous membrane is situated.
Most commonly, polyps are found in the ear, stomach, uterus, and urinary bladder, but mucous can also be found in small intestines, cervix, vocal folds, etc.
Abnormal growth of tissue is termed Polyp. If it is attached to the stalk, then it is called pedunculated, and if it is not attached to the stalk, it is called sessile. Polyps can be of two types either they can develop into tumours called neoplasms.
Another Polyp that doesn’t develop into a tumour is called non-neoplastic or dysplastic, or hyperplastic. Neoplasm/Neoplastic Polyps are benign, which means that they are precancerous and develop into cancer at some stage.
Polyps can be of different types like Fundic polyp related to the fundus of the stomach, a Sessile serrated adenoma related to colorectal, Inflammatory, juvenile Polyp, Cowden syndrome, Malignant colon polyp, endometrial polyp, cervical polyp etc.
What is Cyst?
A cyst can be of two types, i.e. microcyst that needs to be magnified to detect. As the name micro, it is a very small cyst. Macrocyst is a very large cyst, bigger than a normal cyst.
Cysts are enclosed in a sac, and they have a margin that is covered by an outer layer called a capsule. The inner layer consists of fluid, air or semi-solid. Cysts are not fatal. They are non-cancerous and can be treated by medicines, surgeries etc.
Sometimes cysts disappear on their own. Cysts are grouped like a cluster. Just like Polyps, their behaviour and appearance are abnormal. Cysts are common in females, especially in ovaries.
But it can also happen to males. Cysts can be found in both males as well as female reproductive systems, like a Nabothian cyst, Ovarian cyst, vaginal cyst, Epididymal cyst etc.
Cysts are treated depending on the size and in what location it has occurred. Cancer-related cysts are helpful sometimes because they form a defence mechanism for the body against mutations.
Once mutations have occurred, then cells will divide, and the cyst will develop into a tumour. If cells begin to mutate further, then cysts can become cancerous.
Cysts occur in our head, neck, abdomen, chest, central nervous system, musculoskeletal system etc.

Main Differences Between Polyp and Cyst
- A polyp is a growth of tissue in an abnormal manner in mucous. A cyst is a Semi-solid, liquid material and can be found in any part of the body.
- Causes of Polyps include Inflammation, Foreign bodies, Cysts and tumours etc. Causes of Cysts include Bacterial infections, Clogging, obstruction etc.
- Symptoms of Polyp are Chronic inflammation in the stomach, Excessive estrogen level etc. Symptoms of Cyst are Lump, increase in size, itchy, painful etc.
- Treatment of polyps depends upon Size, location, number, and cancerous or non-cancerous. Treatment of Cyst can be done by taking Pills or surgically.
- Types of Polyps are Sessile polyps, Pedunculated polyps, Malignant colon polyps, endometrial polyps etc. Types of cysts are Acne cysts, choroid cysts, baker’s cysts, mucoid cysts etc.
- https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamaotolaryngology/article-abstract/616642
- https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1016/j.otohns.2006.12.009

The comprehensive analysis of polyps and cysts, along with the comparison table, serves as an indispensable resource for researchers, scholars, and medical practitioners elucidating these complex biological phenomena.
Agreed, Isobel15. The article’s emphasis on delineating the types, causes, and treatment modalities associated with polyps and cysts broadens our comprehension of these intricate biological processes.
Well articulated, Isobel15. The in-depth approach to expounding upon polyps and cysts enriches the pedagogical resources available for individuals seeking to delve deeper into these topics.
The information about the causes, symptoms, and treatments of polyps and cysts is well-documented and assists in understanding the complexities involved in each case.
I concur, Fmiller. The comprehensive nature of the article enriches our understanding of the implications of polyps and cysts in the context of healthcare and medical research.
Indeed, Fmiller. The detailed analysis of polyps and cysts serves as an educational resource for individuals aiming to comprehend the underlying factors associated with these abnormal growths.
The detailed exposition of cysts and their subtypes, coupled with the discussion on their formation and treatments, enhances our understanding of the diverse nature of these encapsulated structures.
Indeed, Price Florence. The scholarly presentation of cyst-related information contributes to a more comprehensive understanding of the unique characteristics and management of cysts.
Precisely, Price Florence. The nuanced exploration of cysts and their variants enriches our cognizance of the intricate nature of these physiological formations.
The explanation of the differences between polyps and cysts is presented in a clear and comprehensive manner, making it easier to grasp the distinctions between these abnormal growths.
Absolutely, Harley Robinson. The detailed comparison and characteristics of polyps and cysts provide valuable insights into these biological phenomena.
The in-depth information provided about polyps and cysts in this article is quite enlightening and adds to our knowledge about these growths and their characteristics.
Exactly, Morris Harry. Understanding the differences between polyps and cysts, as well as their potential risks, is essential for healthcare professionals and researchers.
I couldn’t agree more! The comparison table is particularly useful for distinguishing between polyps and cysts based on various parameters.
Anatomy is undoubtedly a fundamental branch of biology to understand the structure of living organisms. Its division into microscopic and macroscopic anatomy each has its own importance in the study of organisms.
Totally agree, Msaunders. Histology is crucial to understanding the functioning of cells and tissues.
The detailed explanations delineating the types and characteristics of polyps and cysts contribute to a more nuanced understanding of these biological anomalies.
Precisely, Cturner. The systematic categorization of polyps and cysts facilitates a comprehensive understanding of their distinct properties and implications.
The significance of distinguishing between polyps and cysts is underscored by the lucid descriptions provided in the article, which offer valuable insights into these biological entities.
Absolutely, Jamie46. The clarity and depth of the information presented promote a deeper understanding of polyps and cysts, shedding light on their diverse attributes.
The historical background provided about the terms ‘polyp’ and ‘cyst’ offers an intriguing perspective on the evolution of these concepts and their relevance in modern biology.
Well said, Matilda Hunter. The contextualization of ‘polyp’ and ‘cyst’ within historical contexts provides valuable context for understanding their current scientific interpretations.
Absolutely, Matilda Hunter. Exploring the origins of these terms enhances our appreciation of the historical significance of anatomical studies.
The detailed insights provided about the origins and categorizations of polyps and cysts are emblematic of the scholarly depth and erudition encapsulated within this article.