Different types of materials had manufactured and designed.
In developing technology, many companies design several materials for decoration purposes. Most of the idols and designed materials had to attract the citizens in the present day. Sculpture and ceramics are the two different designed processes that attract people.
Key Takeaways
- The sculpture refers to creating three-dimensional forms from various materials such as stone, metal, or wood, while ceramics refers to objects made from clay shaped and hardened by heat.
- Sculptures are larger and are used for decoration or public art, while ceramics are more miniature and used for functional purposes such as pottery, dishes, and tiles.
- Sculptures can be made using various techniques such as carving, molding, and casting, while ceramics are made by shaping clay on a pottery wheel, molding, or using other methods.
Sculpture vs Ceramic
Sculpture is a type of art. There are four main materials which are used in the formation of sculptures. Mostly stone is used to make sculptures. It did not break easily. The basic elements to consider while making a sculpture are space and mass. Ceramics is a type of inorganic material. A high temperature is required to model ceramic.

The sculpture is a plastic art that operates in two or three dimensions. Several designed concepts take shapes and form sculptures. The sculpture is the fork of visual arts that manages in three dimensions.
Sculptural processes occur in stone, metal, ceramics, and wood. The sculptural process had used by carving and modelling. A stone can be modelled and shaped as a different structure.
Since modernism, the sculptural process had complete freedom of materials. Several types of stones had used to make sculptures.
Ceramics is a non-metallic material that had shaped into different materials. Ceramics are hard, brittle, corrosion-resistant materials modelled by shaping and firing non-metallic minerals.
Ceramic materials had formed at high temperatures by using non-metallic mineral-like clay. Ceramics is an inorganic material that consists of crystalline oxide, nitride or carbide and elements like carbon or silicon.
Ceramic materials include porcelain, earthenware, brick, tiles, glass, and cement. Ceramics are hard and chemically non-reactive materials that have densified with heat. Ceramics are longer than pottery materials.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Sculpture | Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | The sculpture is the fork of visual arts that manages in two-three dimensions. | Ceramic is a solid, corrosion-resistant material had modelled by shaping and then firing the non-metallic minerals. |
| Kinds | Stone carving, Wood carving, bronze casting, clay firing are the four basic kinds that form the sculptures. | Pottery, Porcelain, Earthenware and Bone China are the four basic kinds of Ceramics. |
| Features | Sculptures are mostly stone made materials and do not break easily. | Ceramics consist of large pores in bricks which breaks easily. |
| Elements | Mass and Space are the main elements to design the sculptures. | Ceramics contain combinations of metallic elements and carbon, oxygen, nitrogen or sulfur. |
| Examples | Venus of Willendorf, Laocoon and his sons, Bust of Nefertiti and many others are examples. | Clay, bricks, tiles, glass, cement are examples. |
What is Sculpture?
The sculpture is the fork of visual arts that manages in two-three dimensions. Several materials like stones, metals, wood, and ceramics had used for the sculptural processes. Sculptural processes had used by carving and modelling.
A stone can be modelled and shaped as a different structure. Since modernism, sculptural processes had complete freedom of materials. Sculptures are represented by carving, casting, and shaping techniques.
An artist forms the sculptures on hard or plastic materials where two-three-dimension sculptures had shaped. Sculptures had mostly made with types of stones that cannot break easily.
Mass and Space are the primary elements for sculptural processes where a substance consists of mass and exists in three-dimensional spaces.
Stone Carving, Wood carving, Bronze Casting, and Clay firing are the four primary methods used in sculptural processes. The sculpture consists of various apps for training. Cinema 4D, Modo, 3D Cat, Blender, Mudbox, and ZBrush are the top seven apps used for 3D sculptural artists.
In the Classical period, Greece produced masterpieces of sculptures. Sculptures originated from the Western tradition.
The idols like Barbies, Goddesses, and famous people are examples of sculptures. In the Middle Ages, Christian people choose Gothic Sculpture to represent agonies and passions. Examples of the Sculptures are,
- Venus of Willendorf
- Laocoon and his sons
- Bust of Nefertiti
- Roman Sculpture
In a word, Sculptures are the art of making statues by carving. Sculptures are famous statues shaped by artists.
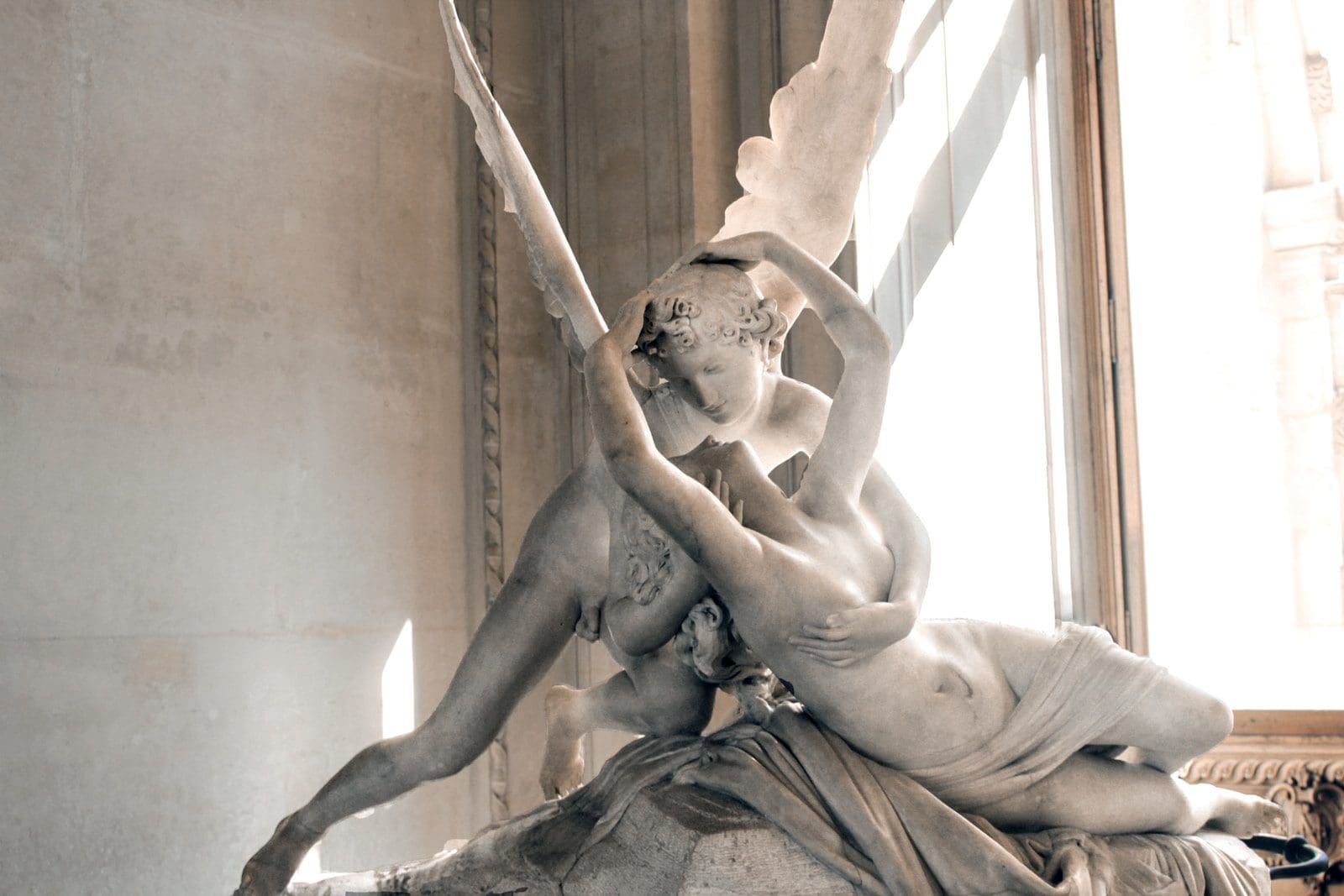

What is Ceramic?
Ceramics are hard, brittle, corrosion-resistant materials modelled by shaping and firing non-metallic minerals. Ceramics is an inorganic material that consists of crystalline oxide, nitride or carbide and elements like carbon or silicon.
Ceramics had been modelled at high temperatures. Non-metallic minerals like clay and bricks had used for shaping the ceramics at high temperatures. Ceramics are hard and chemically non-reactive materials that have densified with heat.
Ceramics are longer than pottery materials. They consist of large pores where ceramics are easily breakable at the pores. Ceramics are different from pottery. Ceramics contains a combination of metallic elements and oxygen, nitrogen, carbon or sulfur.
Pottery, Porcelain, Earthenware and Bone China are the basic kinds used for modelling Ceramics. Ceramics consists of very high melting point temperatures compared to metals and polymers.
The melting point of the Ceramics is 2000 degrees Celsius, where ceramics had modelled at high temperatures.
The Child Material Class of Ceramics is Glass and Aluminum oxide. High Melting Point, Hardness, Strength, long-lasting durability, less consumption of electricity and unreactive are known as Ceramic characteristics.
Ceramics had stored in decorative, waterproof, paint-like substances. Examples of Ceramics are,
- Tiles
- Roofs
- Bathrooms
- Kitchenware
- Artificial bones and Teeth
- Electronic Devices.
An individual can find Ceramic material in daily life. Ceramics had also used for presentations at parties.
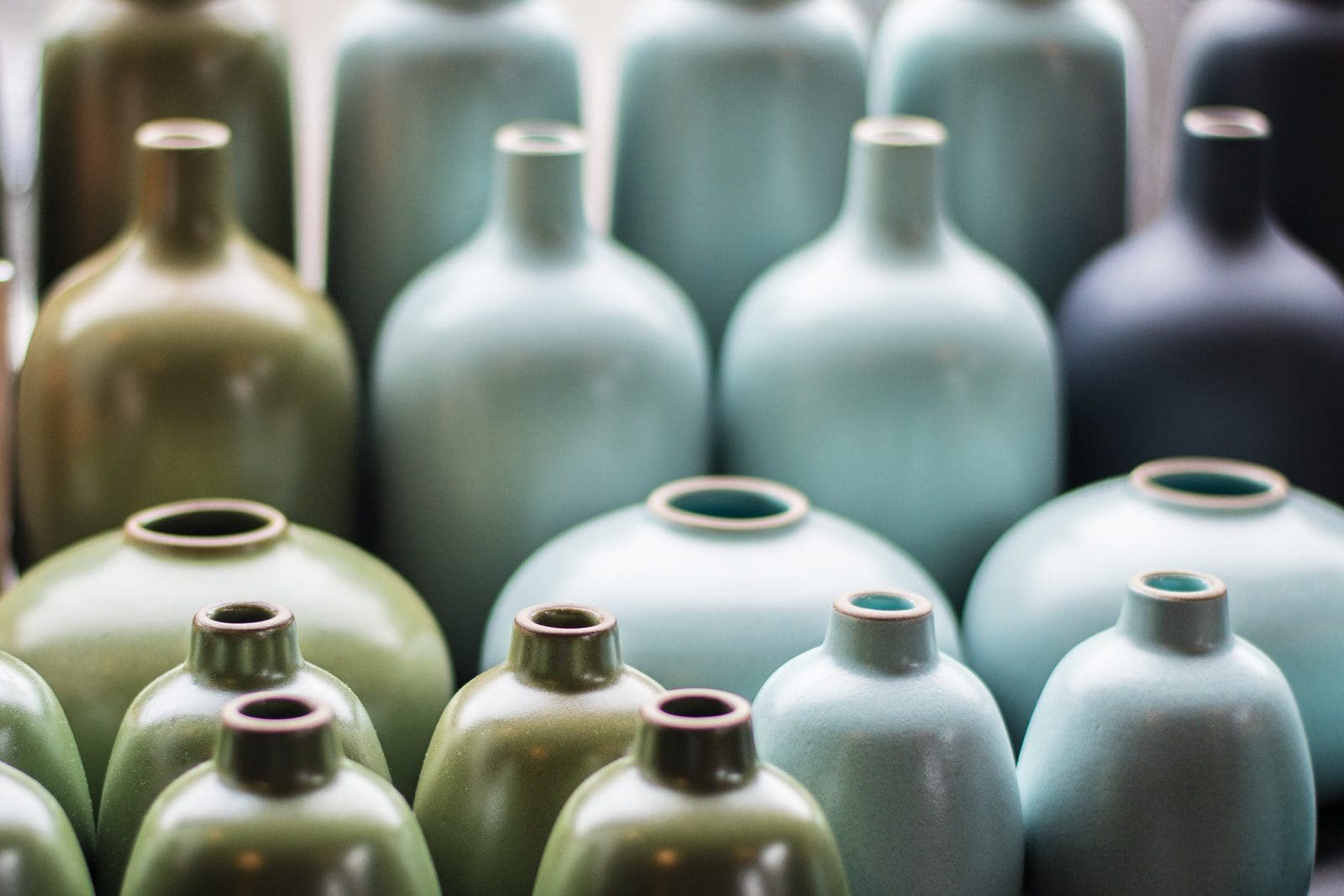

Main Differences Between Sculpture and Ceramic
- The sculpture is a fork of visual arts where Ceramic is a solid, brittle material shaped and fired by non-metallic minerals.
- Stone carving, Wood Carving are the two basic methods used for sculptural processes. On the other hand, Pottery, Earthenware are the main basic methods used for shaping Ceramics.
- Mass and Space are the main elements used to design the sculptures, where Compounds of elements and carbon, and oxygen are the elements that help shape the Ceramics.
- Sculptures do not break easily, whereas some of the Ceramics break easily at large pores.
- Venus of Willendorf and Roman Sculpture are examples of Sculptures. On the other way out, Tiles, Electronic Devices, and Kitchenware are examples of Ceramics.

The comprehensive comparison between sculptures and ceramics, along with the detailed parameters of comparison, is very enlightening. The information about the different types of ceramics, such as porcelain and glass, is particularly informative.
I found the historical context provided for sculptures and the discussion on the different materials used for sculptural processes to be very compelling. The examples of ceramics, including earthenware and tiles, offer a well-rounded understanding of the art form.
I completely agree. The detailed explanation of the sculptural processes and the materials used, especially the mention of stone carving and casting, is very educational. The examples of famous sculptures further enrich the content.
The comprehensive comparison of sculpture and ceramics, along with the detailed explanation of sculptural processes and ceramic materials, is highly informative. The examples of famous sculptures and ceramics further enhance the content.
I completely agree. The comparison table effectively illustrates the distinctions between sculpture and ceramics, while the examples of sculptures and ceramics provide a well-rounded perspective. The historical context of sculptures adds depth to the discussion.
The detailed comparison of sculpture and ceramics, along with the historical context provided for sculptures, is highly informative. The mention of different methods used in sculptural processes, such as stone carving and molding, greatly enriches the understanding of sculpture.
I completely agree. The examples of ceramics, including brick, tiles, and glass, provide a well-rounded perspective on the art form. The comparison table effectively highlights the distinctions between sculpture and ceramics.
The distinction between sculpture and ceramics, with examples of notable works, is very well-explained. The explanation of ceramics, including its composition and examples, provides a comprehensive overview of the art form.
I completely agree. The detailed comparison table really helps in understanding the differences between sculpture and ceramics. The examples of sculptures and the historical context provided are also very engaging.
The detailed explanation of the sculptural processes, including stone carving and casting, offers a comprehensive understanding of sculpture. The historical context provided for sculptures, along with examples of notable works, is particularly engaging.
I completely agree. The detailed description of ceramic materials, including porcelain and earthenware, is highly illuminating. The thorough overview of sculptural processes and the emphasis on materials used greatly enriches the content.
The comparison of sculpture and ceramics is very enlightening. It’s interesting to learn about the different materials and processes used in both art forms. The history of sculpture and examples provided are very useful.
I completely agree. The information about the training apps and the artistic practice of sculpture in the Classical period was particularly intriguing.
I found the details about ceramics and the different types of ceramics, like porcelain and earthenware, to be quite intriguing. The comparison table is a great way to illustrate the differences between sculpture and ceramics.
The detailed explanation of sculpture and ceramics, with an emphasis on the artistic and functional purposes of each, is very informative. It provides a comprehensive overview of both art forms, including materials and techniques used.
The examples of famous sculptures, such as the Venus of Willendorf and the Roman Sculpture, along with the explanation of ceramics and its different types, are highly engaging. The comparison table is particularly useful for understanding the distinctions between sculpture and ceramics.
The explanation about mass and space as primary elements for sculptural processes is thought-provoking. The overview of the primary methods used in sculptural processes is very informative.
I completely agree. The mention of different apps used for 3D sculptural artists was surprising and educational at the same time. The historical context provided for sculptures was also fascinating.
The detailed explanation of sculpture and ceramics, including their composition, properties, and examples, provides a comprehensive understanding of both art forms. The comparison table is particularly useful in highlighting the differences between sculpture and ceramics.
The explanation of sculptural processes and the different materials used, such as stone, metal, and wood, is highly educational. The historical context provided for sculptures, along with examples of famous works, adds depth to the content.
I completely agree. The thorough explanation of ceramic materials, including porcelain and earthenware, and the mention of sculptural processes like carving and modeling, offers a comprehensive overview. The examples of famous sculptures further enrich the content.
The detailed description of sculptural processes and the different materials used, particularly stone, metal, ceramics, and wood, offers a rich understanding of sculpture. The historical context provided for sculptures is particularly intriguing.
I completely agree. The explanation of ceramic materials, including porcelain and glass, along with their properties, is very well-articulated. The reference to sculptural apps and training methods provides a comprehensive perspective of the art form.
The examples of sculptures and the overview of different methods used in sculptural processes are very illuminating. The historical context provided for sculptures and ceramics is particularly engrossing. The comparison table is a great addition to the content.