The two most important terms in the analysis are measurement and evaluation.
Both these terms have monumental value in all platforms, from business to academic, where determining performance or differences play pivotal roles.
Although perceived as the same, measurement and evaluation differ. While one is prized for calculations, another is valued for performance analysis.
Key Takeaways
- Measurement is determining the quantity, size, or extent of a variable or attribute using standardized tools, scales, or units.
- Evaluation is the systematic process of assessing the quality, value, or effectiveness of something based on specific criteria or standards.
- Both measurement and evaluation involve gathering and analyzing information, but measurement focuses on quantifying attributes, while evaluation is broader, encompassing the interpretation and judgment of the measured data.
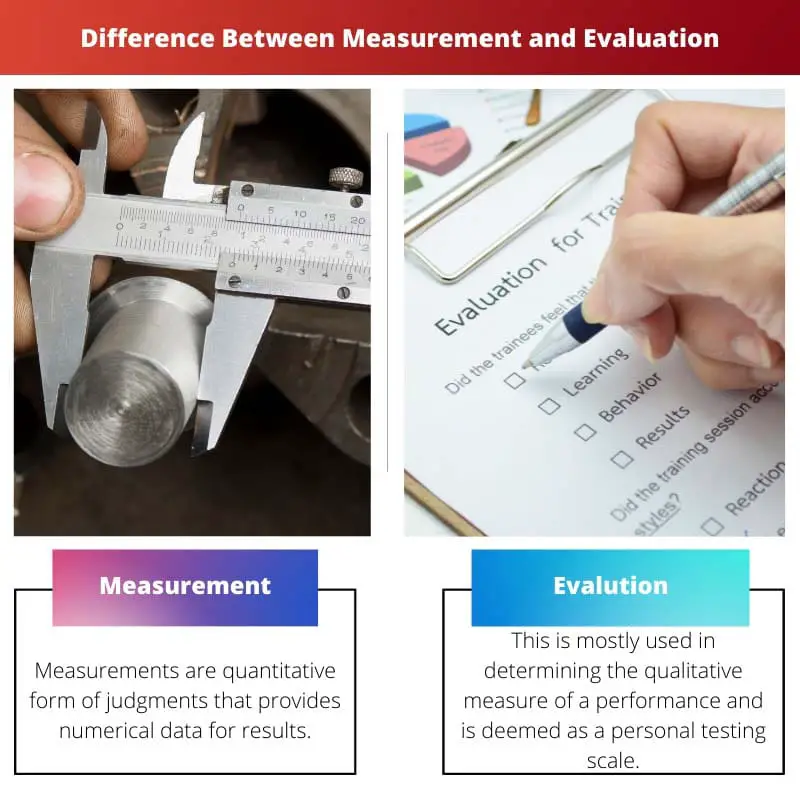
Measurement vs. Evaluation
Measurements are quantitative forms of judgments that provide numerical data for results. It helps in determining performance and also useful in tests such as personality tests. Evaluation is a testing tool that is used in determining the qualitative measure of a performance and is deemed as a personal testing scale.

Measurement involves specifications, whereas evaluation is relative to something considered standard. While measurements only determine the magnitude of a different evaluation adds value to that difference.
However, measurement provides the data and the basis for evaluation.
Another way to state the difference between measurement and evaluation is to say measurement is scientific, whereas Evaluation is philosophical.
Measurement involves determining differences in numbers, while evaluation is a more personal form of judgment.
Evaluation adds value to the mere numerical data provided by measurements.
Comparison Table
| Parameter of Comparison | Measurement | Evaluation |
|---|---|---|
| Type of Judgment | Measurement is Objective | Evaluation is Subjective |
| Use of Number | Provides numerical data | Uses numerical data to provide value-added results |
| Nature | Scientific in nature | Philosophical in nature |
| Form of Data | Quantitative form of data | Qualitative form of data |
| Results represent | Magnitude of variant | Value of the magnitude |
What is Measurement?
Measurements are a quantitative form of judgment that provides numerical data for results. They are subjective and specific. They are mostly used for data collection and provide the basis for further analysis.
Measurements are mostly the magnitude of height, weight, length, breadth, and circumference, whose units can be determined by specific numbers. Measurements are followed by units that define what the number denotes.
From economy to architecture, military to astronomy, measurements that provide numerical data are pivotal to every profession.
Although priceless to human existence in the twenty-first century, measurements are the only objective means of determining their worth. They are a form of scientific judgment that is specific.
Measurements are used for data collection, determining the size, amount, or quantity by a numeric figure.
This is thus helpful in determining performance where objective evaluation is the focus, such as a score in an exam, the time difference between two countries, or the amount of money in a bank account.
Measurement is also useful in tests such as personality tests, testing one’s intelligence quotient, or average score in a game.

What is Evaluation?
Evaluation is an objective testing tool. This is mostly used in determining the qualitative performance measure and is deemed a personal testing scale.
Evaluation is relative, and it adds value judgment to a numerical variant. Evaluation results do not carry any unit and are used to determine the performance relative to a standard or based on past performance results.
Evaluation has an emotional factor attached and is not always specific. They are deemed to be philosophical.
Evaluation can measure one’s behavior and consider genetic factors, likes and dislikes, inclinations and biological patterns, etc., to determine the result.
Evaluation is comprehensive, where all the numerical data from measurement is interpreted into descriptive results. Evaluation incorporates several techniques that trained personnel use to determine value-added results.
Unlike measurement, an evaluation measures a pupil‘s true worth, where the skills and achievements are judged based on the objectives above.
Evaluation is not just assigning scores or average marks but interpreting these numbers to determine a student’s worth.
Evaluation is an efficient tool to measure one’s mental abilities, ideas, outlook and frame of mind, habits, and conduct. Evaluation can determine the qualities and interpret their results and scope for improvement.

Main Differences Between Measurement and Evaluation
- The main difference between measurement and evaluation is that measurement is a quantitative value, whereas evaluation is a qualitative description.
- Another difference between the two is a measurement is an objective form of measure while evaluation is a subjective form.
- Measurement involves specifications, whereas evaluation is relative to something considered standard. The standard for evaluation may vary from person to person.
- The difference between measurement and evaluation is that measurement is scientific, whereas Evaluation is philosophical.
- Measurement involves determining differences in terms of numbers, while evaluation adds value to the mere numerical data provided by measurements.
- Measurement is useful in determining personality tests and testing one’s intelligence quotient or average score in a game. Evaluation measures one’s mental abilities, ideas, outlook and frame of mind, habits, and conduct.
- https://psycnet.apa.org/record/1984-10995-001
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/j.1556-6676.1992.tb01631.x

This article provides a comprehensive and informative analysis of measurement and evaluation. The distinctions are well-highlighted and contribute to a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
Indeed, Liam89. The article encapsulates the essence of measurement and evaluation with exceptional clarity.
Liam89, I couldn’t have said it better myself. The thoroughness of the article is commendable.
The detailed explanations of measurement and evaluation are enlightening. This article effectively clarifies the nuances between the two concepts.
The article does an excellent job of contrasting measurement and evaluation. The comparison table is particularly helpful. Well done!
Absolutely, Reid Bethany. The clear distinction between quantitative and qualitative aspects is informative and insightful.
I’m glad to see a thorough breakdown of the differences. This article is an essential resource for understanding measurement and evaluation.
The comparison between measurement and evaluation is very well-articulated. The clarity and depth of analysis make this article a valuable read.
I couldn’t agree more, Xchapman. The depth of analysis in this article elevates the understanding of measurement and evaluation.
Absolutely, Xchapman. This article presents the topic with precision and thoroughness.
The article offers a comprehensive and in-depth exploration of measurement and evaluation. The differentiation between the two concepts is articulated with exceptional clarity and scholarly insight.
Aparker, I wholeheartedly agree with your assessment. The article’s scholarly approach to the subject matter is truly commendable.
The detailed explanations regarding measurement and evaluation are insightful and thought-provoking. This article effectively communicates the key differences between the two concepts.
I completely agree with you, Craig29. The comprehensive nature of the explanations enriches the understanding of measurement and evaluation.
The comparison table effectively summarizes the essential differences between measurement and evaluation. The article is a valuable resource for understanding the intricate nuances of these terms.
I share your sentiments, Vwilson. The comparison table adds significant value to the comprehensive analysis.
The article’s emphasis on the key differences between measurement and evaluation is highly informative. The explanations are delivered with precision, enhancing the readers’ understanding of these concepts.
Neil, your assessment is spot-on. This article is an invaluable resource for anyone seeking clarity on measurement and evaluation.
I echo your sentiments, Robinson Neil. The article’s treatment of measurement and evaluation is exemplary.
Great article! It provides a clear and concise explanation of the differences between measurement and evaluation. I appreciate how it breaks down the definitions and key takeaways.
Abbie Butler, I couldn’t agree more! This article offers valuable insights into the subject matter, making it easy to understand.
The article conveys a clear and thorough understanding of measurement and evaluation. The detailed breakdown of the two concepts is commendable and enriches the readers’ knowledge.
Absolutely, Jackson Chelsea. The article’s exploration of measurement and evaluation is exemplary.
Jackson Chelsea, I couldn’t agree more. The clarity and depth of analysis in this article are praiseworthy.