Nebulae and galaxies are astronomical deep-sky phenomena that are seen by telescope only. All kinds of phenomena are seen as fluid spots in the night sky from the naked eye or a low-power telescope.
Therefore, confusions remain in the early phases of the history of astronomy and still today, in some cases. A nebula is a deep-room fog composed of gas or dirt (e.g., a cloud formed after a star explodes).
The galaxy is defined as a collective of many stars, dust, planets, and other interstellar matter linked to a gravity force.
Key Takeaways
- A nebula is a cloud of gas and dust in space, the birthplace of stars.
- A galaxy is a massive collection of stars, gas, and dust held together by gravity.
- Nebulas are much smaller than galaxies and are found within galaxies.
Nebula vs Galaxy
Nebula is a group of carbon, oxygen and nitrogen gasses. It is in the form of a cloud. Nebulae can be seen in the sky at night. They can be of different colors. Nebulae are of three main types. A galaxy is a huge collection of stars. Galaxies are categorized on the basis of their forms. There are two main groups of galaxies.

Nebula is a deep-room fog of gas or dirt/dust. The Latin word Nebula, “cloud,” was derived from that word. Often known as nebulae are nebulae. The nebula is known as dust and gas clouds.
Earlier, astronomers have named galaxies nebula because of their fluidity. The term nebula is still used, however, for long structures composed mostly of gas and dust. It is available in several different shapes and sizes and shapes.
A galaxy is a group of stars, dust, planets, and other interstellar matter linked by gravity is called a galaxy. Any number of elements can comprise a Galaxy. For instance, a small Galaxy can consist of only a couple of thousand stars, whereas a big Galaxy can have billions of stars.
Milky Way’s a Galaxy Example; it’s our Earth and our Sun’s Galaxy. Only identified and observed Galaxies in the Universe can be provided by astronomers. However, in the entire universe, there may be different Galaxies.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Nebula | Galaxy |
|---|---|---|
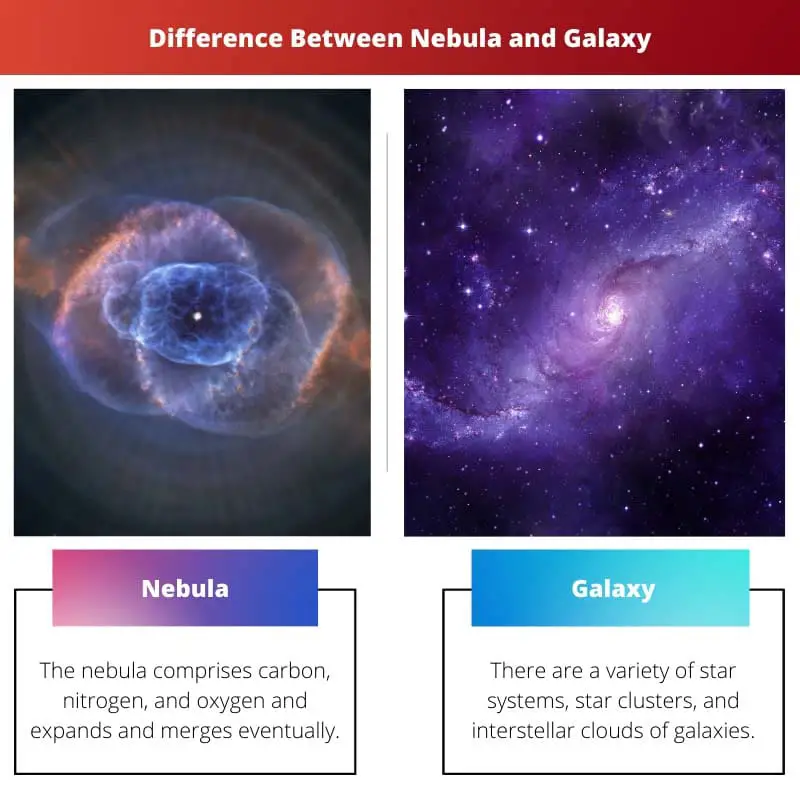
| Component | The nebula comprises carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen and expands and merges eventually. | There are a variety of star systems, star clusters, and interstellar clouds of galaxies. |
| Formed | A nebula is a deep-room fog of gas or dirt/Staub (e.g., a cloud formed after a star explodes). | A collective of various stars, dust, planets, and other interstellar matter is known as the Galaxy. |
| Discovered By | Huggins discovered Cat’s Eye Nebula. He was the first to analyze the spectrum of a planetary nebula. | Edwin Hubble studied the galaxies extensively by classifying and categorizing them based on their form and composition. |
| Meaning | Nebula is an interstellar disc of dust. | Galaxy is an enormous array of stars. |
| Size | Nebula is small. | Galaxy is big. |
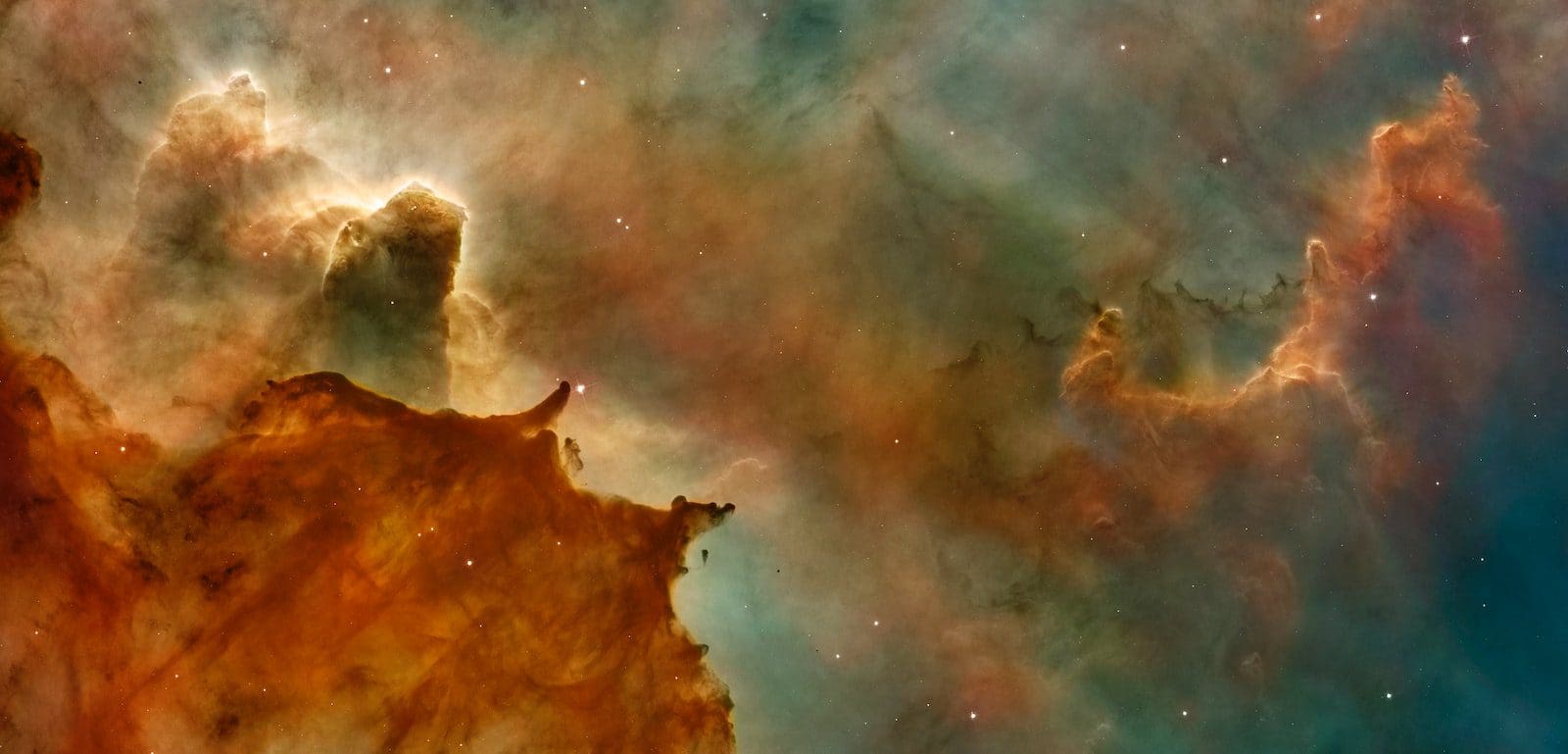
What is Nebula?
Nebulae are a broad group of cosmic gas and fragments of dust. Most nebulae can be construed as a denser area of the interstellar medium that accretes below gravity; others remain of stars after their lifespan.
The primary components are helium and hydrogen. However, there could be other components of different quantities.
The nebula will ionize the gases in the nebulae when located near extremely active astronomical objects, including young stars and other forms of radiation sources. Nebulae are also seen in the night sky as luminous spots.
They come in several different colors, which form and sometimes correspond to common names like Cat’s Eye, Ant, California, Horse Head and Eagle nebulae, and other astronomical names.
Emission nebula, dark nebulae, and reflection nebulae are three major types of nebulae. Nebulae of emissions are interstellar clouds with a characteristic spectrum of emission lines.
The thick interstellar medium surrounding the black holes, an energy source, such as hot young stars and accretion discs, ionizes, and the excited gases emit radiation of various wavelengths. We look like a nebula in this area.
The Orion nebula, the third apparent star of the Hunter, is a classy example of the emission nebula of the Hunter. The nebula of Orion is about 1500 light-years in the night sky.
It has about 300 solar material masses and is an area of young stars of type O and B that are formed in the nebula. The gases light from these young stars. The Trapezium is defined as four visible light stars in the nebula.

What is Galaxy?
Huge star collections and vast interstellar gas clouds constitute the galaxies. Until the late 18th and 19th centuries, the great superstructures of the star were not adequately defined and observed.
They are then thought of as nebulae. These star collections lie outside the Milky Way. This is our star collection. It is also hard to differentiate between a naked eye or a small telescope between galaxies and nebula.
Most night sky phenomena are part of our galaxy; if you look carefully, the twin galaxy of the Milky Way, the Andromeda Galaxy, may be identified. Edwin Hubble studied the galaxies extensively by classifying and categorizing them based on their form and composition.
The spiral and elliptical galaxies were the two major groups. Spiral galaxies were further categorized as Spiral Galaxies and Barred Spiral Galaxies in two subgroups based on the size of the spiral axes.
Spiral galaxies have centre bulge spiral arms. It is very dense in the middle of the galaxy and is luminous, with a bulb reaching above and beyond the galactic plane.
Because of Spiral arms, these regions are apparent as light winding arcs are regions with a higher sun density too. The radiation of the stars illuminates the interstellar medium in these areas.

Main Differences Between Nebula and Galaxy
- In a star, a nebula is present, whereas the galaxy is not present.
- Various stars’ existence is linked to a galaxy’s life, whereas the life of just one star is related to a nebula.
- Nebula is small, whereas the galaxy is big.
- A nebula is an interstellar disc of dust, whereas a galaxy is an enormous array of stars.
- Huggins discovered Cat’s Eye Nebula, whereas Edwin Hubble studied the galaxies.
- https://www.pnas.org/content/15/3/168.short
- https://inis.iaea.org/search/search.aspx?orig_q=RN:9406020

This article provided a comprehensive overview of nebulae and galaxies, covering both their characteristics and historical significance.
I completely agree, Sarah. The content was both enriching and captivating.
The detailed explanation of the types of nebulae and the role of ionized gases was enlightening.
I agree, Elizabeth. The article delved into the nuances of nebulae beautifully.
The information about the discovery of nebulae and galaxies and their meanings was fascinating.
I agree, the historical context added depth to the article.
A very informative read that has deepened my understanding of these cosmic phenomena.
I’m glad you found it informative, Alex! The examples provided also made the concepts easy to grasp.
This article has further piqued my interest in astronomy. I’d love to learn more about specific nebulae and galaxies.
I appreciate the descriptions of the Orion nebula and the characteristics that make it unique.
The section on the formation of young stars within the Orion nebula was truly captivating.
The detailed analysis of nebulae and galaxies in this article is a great resource for anyone interested in astronomy.
Thanks for the detailed explanation of the differences between nebulae and galaxies!
I’ve always wondered about the distinction between the two, so this was really helpful.
The information about the different types of nebulae was particularly interesting to me.
The explanation of the differences in size and components between nebulae and galaxies was very insightful.
Absolutely, Sophia. This article provided a comprehensive understanding of these celestial bodies.
I found the comparison of the sizes of nebulae and galaxies particularly engaging.
A great breakdown of the key takeaways and features of both nebulae and galaxies.
The comparison table was especially helpful in understanding the differences between nebulae and galaxies.
I appreciate the clear explanation of the key characteristics of nebulae and galaxies.
The details about the discovery and meaning of nebulae and galaxies were presented in a clear and compelling manner.
I couldn’t agree more, Noah. The historical and scientific insights were truly intriguing.
This article has deepened my fascination with the cosmos. I’m grateful for the wealth of knowledge it provided.