Pumps and turbines are a major part of the industrial growth of the world. In industries, many aspects of it would not function without either of them.
They are words commonly seen in textbooks used in mechanical as well as civil engineering and even automobile engineering. For the creation of energy and for transferring the source of power and energy, both pump and turbine turn out effective.
Key Takeaways
- Pumps are mechanical devices that move fluids by increasing pressure or kinetic energy, while turbines convert fluid energy into mechanical energy to generate power.
- Pumps consume energy to transport fluids, whereas turbines harness energy from fluids to produce electricity or drive machinery.
- Pumps are used for applications like water supply, irrigation, and fluid transfer, while turbines find use in power generation, such as hydroelectric, wind, and steam turbines.
Pump vs Turbine
Pumps are devices that move fluids from one location to another, while turbines generate power from a fluid’s kinetic energy. Pumps increase fluid pressure, while turbines convert the energy of a fluid into mechanical or electrical power. Pumps and turbines vary in type and size.
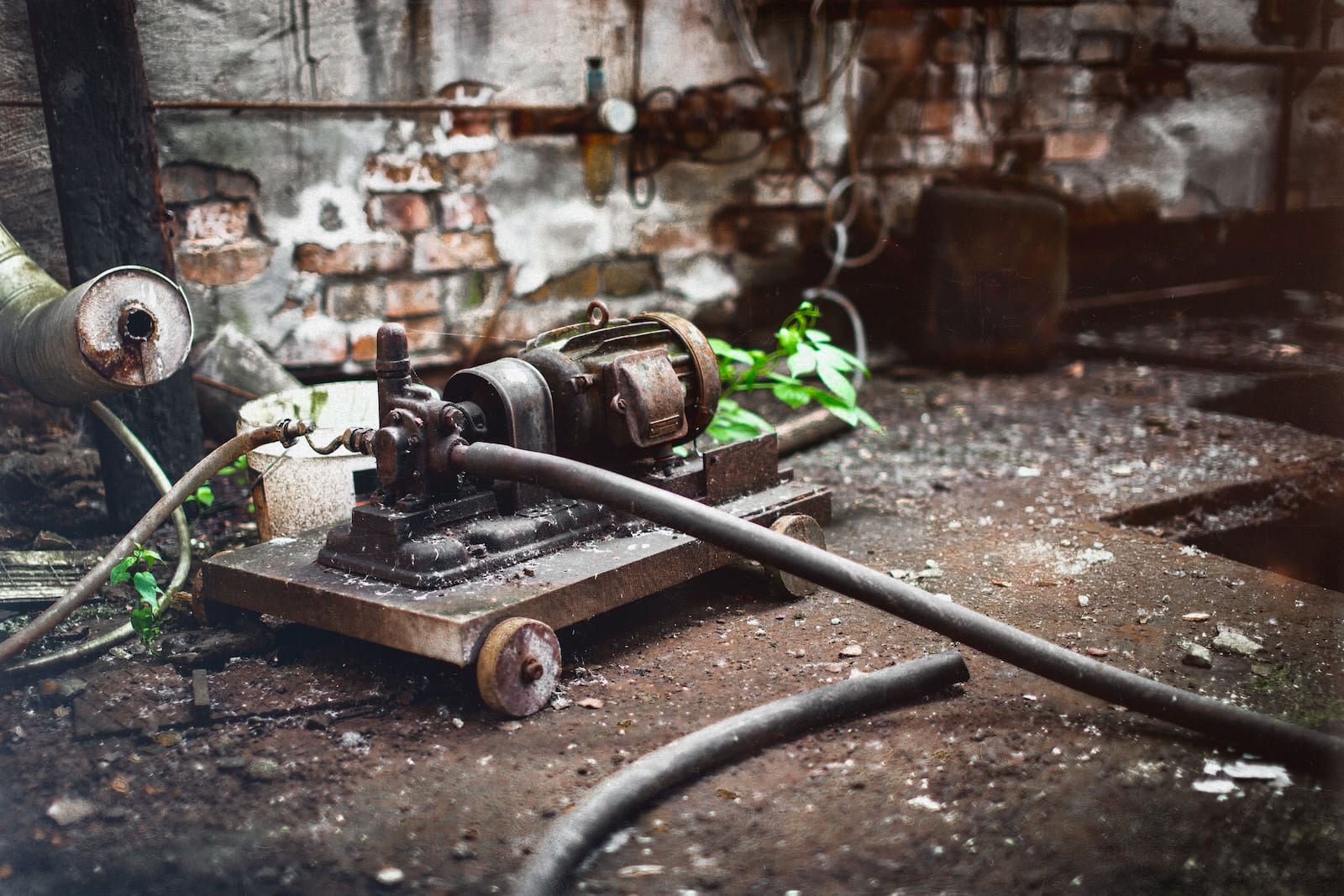
The pump operates based on many practical reasons. The most common motion of a pump engine is rotatory but that doesn’t mean linear motion isn’t used in pumps.
Pumps are not known to use the energy it gains to convert it into other forms. Pumps are not always efficient and there are chances that the energy a pump has can be lost through many different means.
A turbine is a machine that is used to create work while using the energy that it gains through means such as water and solar power.
It is seen in many industries that work as eco-friendly units to create and use the energy produced through unlimited resources such as hydropower. No energy created from a turbine is lost as it is directly converted to work.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Pump | Turbine |
|---|---|---|
| Presence Of Blades | No | Yes |
| Uses Kinetic Energy | No | Yes |
| Uses Mechanical Energy | Yes | No |
| Principle | Linear as well as rotatory motion | Only rotatory motion |
| Examples | Air compressor | Windmill |
What is Pump?
The pump was introduced to ease out the process of pulling up water from borewells and other deep ditches constructed to take out water from the aquifer.
It attains mechanical energy which is used to push up the water from the ground level and bring it after scaling multiple meters in height.But that doesn’t mean a pump is used only for water. It is used for all kinds of fluids including water and air.
While transferring the fluid from one position to another, a pump ensures that the energy state of the fluid is always taken to a higher state.
If a pump reduces the energy state of any fluid that it is supposed to carry, then it could be said that the efficiency of a pump is drastically reduced.
When a pump is in motion, there are high chances that the mechanical energy given to the pump to transport liquid is used for other purposes.
This means that this energy could be utilized for light and sounds and even in the slight motion of pipes through which the liquid is carried.
There are three types of pumps that are commonly seen in places that greatly increase the GDP of a country like factories and industries. These three are lift, displacement, and gravity pumps.
The specialty of a pump is that it cannot convert the mechanical energy to any other form unless the small amount of energy lost is considered.
Therefore the energy stored in a pump is just used on the liquid it transports to create new paths and scale higher heights. Air compressors are a type of lift pump and are seen in air conditioners and a few types of fridges.
Air compressors take the air present in the atmosphere and convert it to different forms by transporting it to the inside of the device.

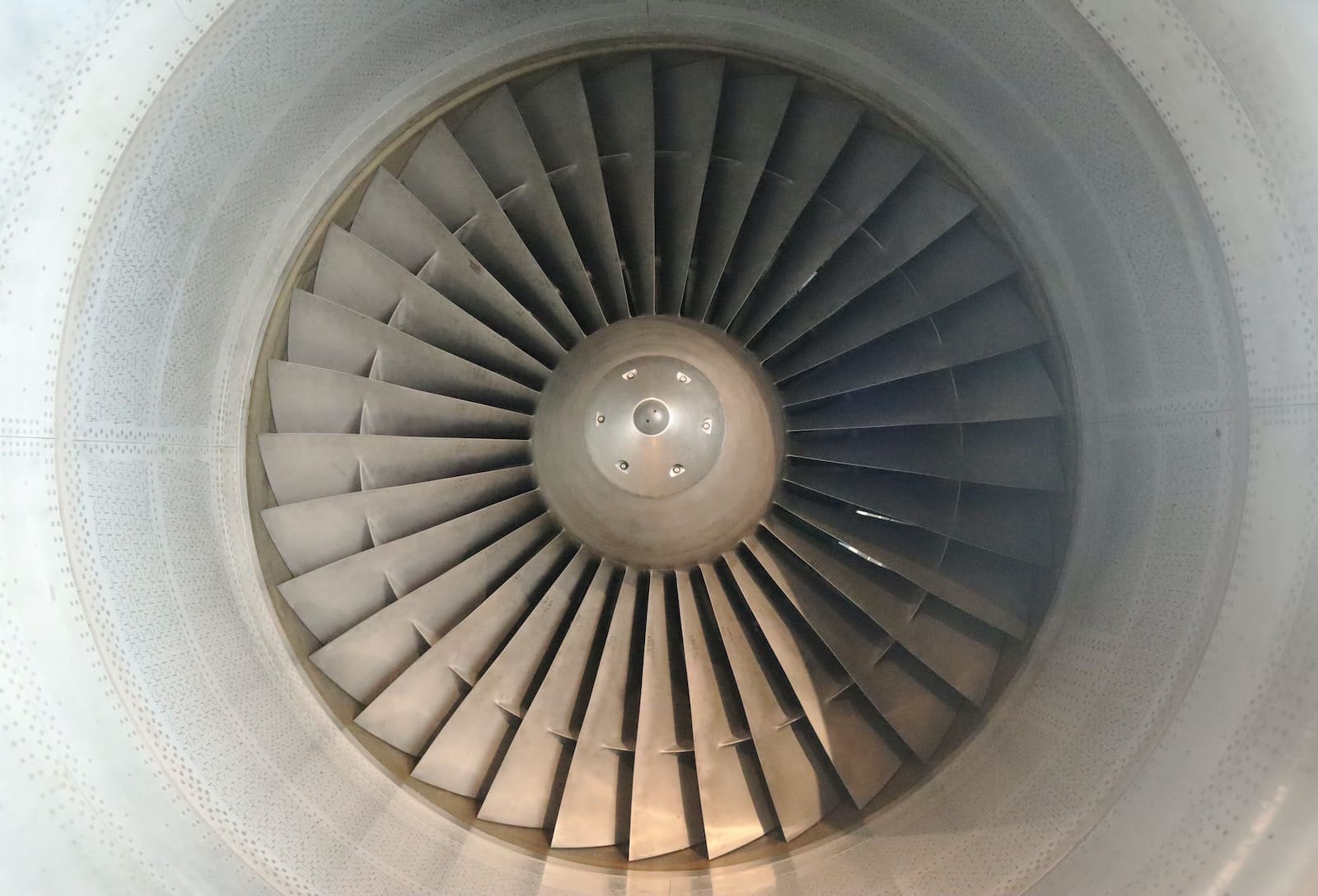
What is Turbine?
Turbines were invented way back in time as a means to generate energy and power to get small-town works done.
Turbines use fluid to generate enough energy by moving the fluid around within an area and ensuring that the fluid crosses paths with all the blades of the turbine.
Turbines have blades that are attached to a single point on the central axle of the turbine which is rotated with every motion.
The blades have a shape like that of a fan and this shape provides enough momentum to extract the maximum possible energy from the fluid that is used.
All turbines are known to be connected to a pump or similar machines that harness the energy from a turbine to carry out a few specified tasks.
Turbines are seen in dams and hydropower stations that are under the government or other private organizations with a massive cash flow.
Windmills and wind-powered activities take the energy formed by the movement of the turbine blades which create mechanical energy that could be converted to work.
The power given to a turbine can be lost to the environment in many forms such as sound and light. The movement of the axle in circular motion might also indicate that friction is another way the energy is lost.
For the turbine to create power in a pump, it has to be connected to a dynamo which transfers the energy to the pump so it can carry out the work assigned to it.

Main Differences Between Pump and Turbine
- While pumps cannot convert the energy it has to other different forms, turbines are capable of converting their energy to other energy forms.
- Turbines are never known to change the energy level possessed by the fluid whereas pumps ensure that the energy level of the fluids is always increased.
- Pumps work on the principle of both rotatory motions as well as a linear motion to carry out work but turbines on the other handwork on the principle of rotatory motion alone.
- A turbine converts kinetic energy to mechanical energy whereas a pump converts mechanical energy to kinetic energy.
- Pumps don’t possess axle and blade to carry out their functions whereas turbines have axles and blades.

- https://journals.aps.org/prl/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevLett.109.233901
- https://books.google.com/books?hl=en&lr=&id=wwplsy8sU6MC&oi=fnd&pg=PP1&dq=turbine&ots=le4p9Z0c4b&sig=Jmkv1pyOBlvLl7kcgwfINcjv_0k
