When humans discuss the field of genetics, there are two terms that capture the topic well: genes and DNA. These two are very important parts of a human being when it comes to genetic and hereditary materials that are passed on to their offspring.
A gene is like a chain or a short section of DNA, whereas DNA is a molecule that carries specific genetic materials. They play a very important role in the body as they instruct the body cells how to work and grow as well as reproduce.
Key Takeaways
- Genes are specific segments of DNA that contain instructions for creating proteins, while DNA is the entire genetic material in a cell.
- DNA has a double helix structure, and genes are organized within this structure.
- Genes determine specific traits in an organism, whereas DNA provides the blueprint for the organism’s overall characteristics.
Gene vs DNA
DNA(deoxyribonucleic acid) is a long, complex molecule that carries genetic information in the form of a code. DNA is found in the nucleus of every cell in an organism. Genes are segments of DNA that contain the instructions for building specific proteins. Proteins are responsible for carrying out most of the functions in living organisms, including metabolism, growth, and repair.

When it comes to hereditary that is functional, we term it as Gene as they are made from DNA and takes up a small part of it to function. Genes are the ones that are passed from the parents to their offspring, which helps in sharing part of the entire DNA molecule.
Genes work in packs or are arranged in a group that is popularly known as chromosomes. A human being has 46 chromosomes, which are in pairs of 23.
DNA or Deoxyribonucleic acid is a biomolecule present in the body that contains most genetic information passed on from the parents to their child or children.
DNA is made or in the structure of two long twisted strands where each comes from the mother and father and acts as a blueprint for all organisms that are living. These two strands in the DNA are called polynucleotides.
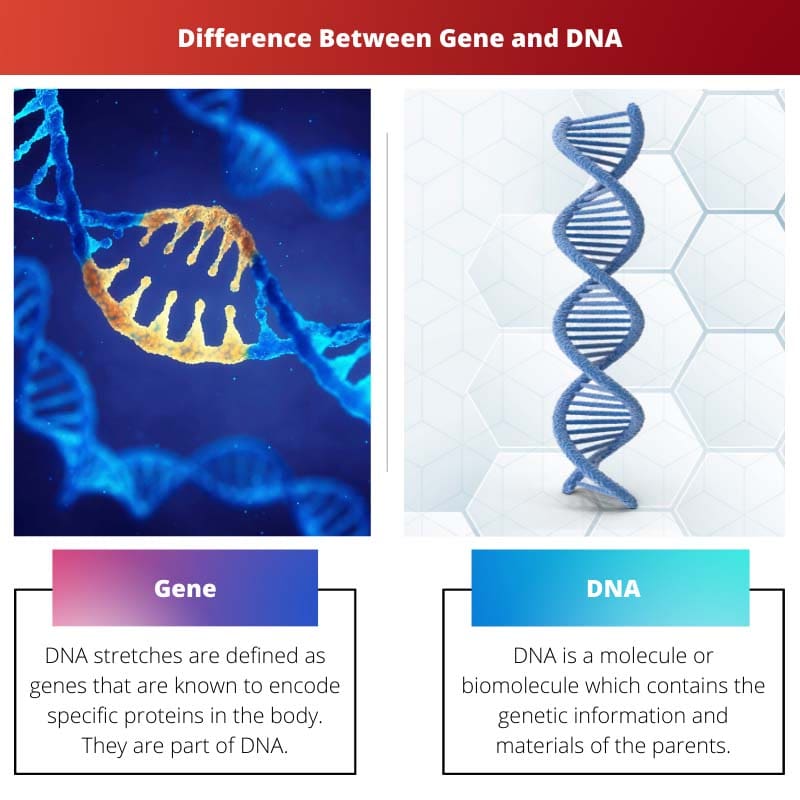
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Gene | DNA |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | DNA stretches are defined as genes that are known to encode specific proteins in the body. They are part of DNA. | DNA is a molecule or biomolecule which contains the genetic information and materials of the parents. |
| Function | Genes function to regulate the traits of any living organism. | DNA functions to regulate the gene regulations in the body of an organism. |
| Location | Found in a chromosome. | Found in the nucleus of a cell. |
| Made of | Genes are made of DNA or RNA. | DNA is made of a polymer of nucleotides. |
| Code | Genes are coded with heredity information. | DNA encodes that genetic information. |
What is Gene?
Genes carry the parent’s information called traits, which contain the features and characteristics of them that are passed onto their children or are inherited by them. These genes are a small section of the DNA that is present in each cell.
There are about 30000-350000 genes present in every cell of the body. Since genes are made of DNA or RNA, it can be said that gene is also a chain of nucleotides in them.
This chain of nucleotides encodes the fusion of gene accumulation, which can either be RNA or protein.
Genes are packed together in each cell, which is called chromosomes, where human beings tend to have 23 pairs of chromosomes or 46 of them. Chromosomes work in a very featured way from both the mother and the father of an organism.
A set of chromosomes are each passed down by the mother and father into their child’s body during reproduction. These genes conduct functions and also play a vital role in managing the functions of DNA or RNA.
When gene expression takes place, DNA is copied to RNA as the first step. This copied RNA functions as the template for a protein that main functions in the body in terms of genes.
An example of gene function through genes is eye color. Genes are very small, and hence we can’t see them, and each gene, which is almost 30000 per cell, has a different job to do as their core function.
They work under specific instructions from DNA.
What is DNA?
DNA, or Deoxyribonucleic acid, is a very integral part of the subject of genetics because it majorly contains all the information needed to build and maintain a living organism on this planet.
Every cell of the body of an organism, especially a multicellular, has a full set of structured DNA.
Johannes Friedrich Miescher, a Swiss biologist, discovered DNA in the year 1869, which showed the complete structure of the DNA molecule, which looks like a twisted ladder at both ends. In other words, DNA can be called genetic material.
DNA is composed of nucleotides containing sugar, and phosphate groups, along with nitrogen bases. These help the DNA to function its part in the body and help transfer genetic information from the parents to the child.
They function in growth, development, and reproduction in the organism’s body.
However, DNA functions more than just specifying the structure and functions of living things as it takes part and plays the role to serve as the primary unit of hereditary of a living organism and many known viruses.
It is said and given that when an organism reproduces, a portion or set of DNA is passed onto their offspring, which ensures the continuity of a specific kind of species from one generation to the other.
However, the DNA from the parents does not form the new DNA of their children, and there is a difference that brings diversity and versatility to the species kind. These allow for subtle changes in the continuity of life.
Main Differences Between Gene and DNA
- Genes are known as a part of DNA stretches that encode proteins in the body, whereas DNA is a biomolecule that participates in the main function of genetic information.
- Genes regulate the genetic information from the parents to their offspring, whereas DNA regulates what gene regulates.
- Genes include DNA or RNA. On the other hand, DNA comprises polymers of nucleotides.
- Genes are coded with hereditary information of the parent organism of both kinds, whereas DNA is coded with genetic instructions that help it grow and work.
- Genes are present in the chromosome of each cell in the body. The DNA is present in the nucleus of each cell of the body.
- https://www.pnas.org/content/98/17/9853.short
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/bdra.20770

The explanation of DNA and its structure is quite enlightening.
Yes, I found it to be very informative.
The explanation of the differences between genes and DNA is well articulated and informative.
Absolutely, I found it very educational.
I agree, it’s very well explained.
The section on the function of genes within chromosomes provided a comprehensive understanding.
Absolutely, it’s very well-written.
The detailed explanation of gene function in relation to the traits inherited from parents was fascinating.
Absolutely, I had a great learning experience.
I agree, it’s a captivating read.
The comparison table between genes and DNA is very useful for clarifying the distinctions.
I found it to be quite a handy reference.
Definitely, it provides a clear differentiation.
The intricate details about the role of genes and DNA in heredity were engrossing.
Absolutely, it’s a fascinating area.
The section on gene expression and the role of RNA in the process is particularly insightful.
Agreed, it really provides a comprehensive understanding.
Yes, the article offers great depth on this topic.
The reference to the role of each gene in the body is quite fascinating.
Agreed, it’s a well-explained concept.
The explanation of DNA and its function in regulating gene expressions was very illuminating.
I found it to be particularly insightful.
The inclusion of practical examples to explain gene function was very helpful.
I agree, it provided great clarity.
Absolutely, it really enhanced understanding.