Catheters are long, flexible, tube-like medical instruments used to administer medicine to a patient directly into the bloodstream for faster and more effective treatment.
Key Takeaways
- Tunneled catheters have a portion placed under the skin, reducing infection risk, whereas non-tunneled catheters enter the body directly at the insertion site.
- Tunneled catheters are suitable for long-term use, while non-tunneled catheters are for short-term use.
- Tunnel catheter placement requires a surgical procedure, while non-tunneled catheters can be inserted at the bedside.
Tunneled vs Non-Tunneled Catheter
The difference between tunnelled and Non-tunneled catheters is that while one is superficial, the other is placed quite deep inside the body. The location and function of these catheters vary. Tunneled catheters are placed under the skin, while Non-Tunneled catheters are placed directly into a large vein.

Tunneled catheters are permanent types of catheters used to deliver medicines to patients incapable of regularly injecting medicines or orally administering the same.
Non-tunneled catheters are temporary types of catheters used to deliver medicines to patients incapable of regularly injecting medicines or orally administering the same.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Tunneled Catheter | Non-Tunneled Catheter |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Tunneled catheters are placed under the skin into a vein. | Non-Tunneled catheters are placed directly into a large vein. |
| Type | Tunneled catheters bare permanently placed. | Non-Tunneled catheters are temporarily used. |
| Insertion | Tunneled catheters are more difficult to place than a Non-Tunneled catheters. | Non-Tunneled catheters are easier to place than a tunneled catheters. |
| Removal | Tunneled catheters are tough to remove. | Non-Tunneled catheters are easier to, remove. |
| Function | Tunneled catheters are used for antibiotic administration, chemotherapy and so on. | Non-tunneled catheters are used for IV therapy, draw large amounts of blood and so on. |
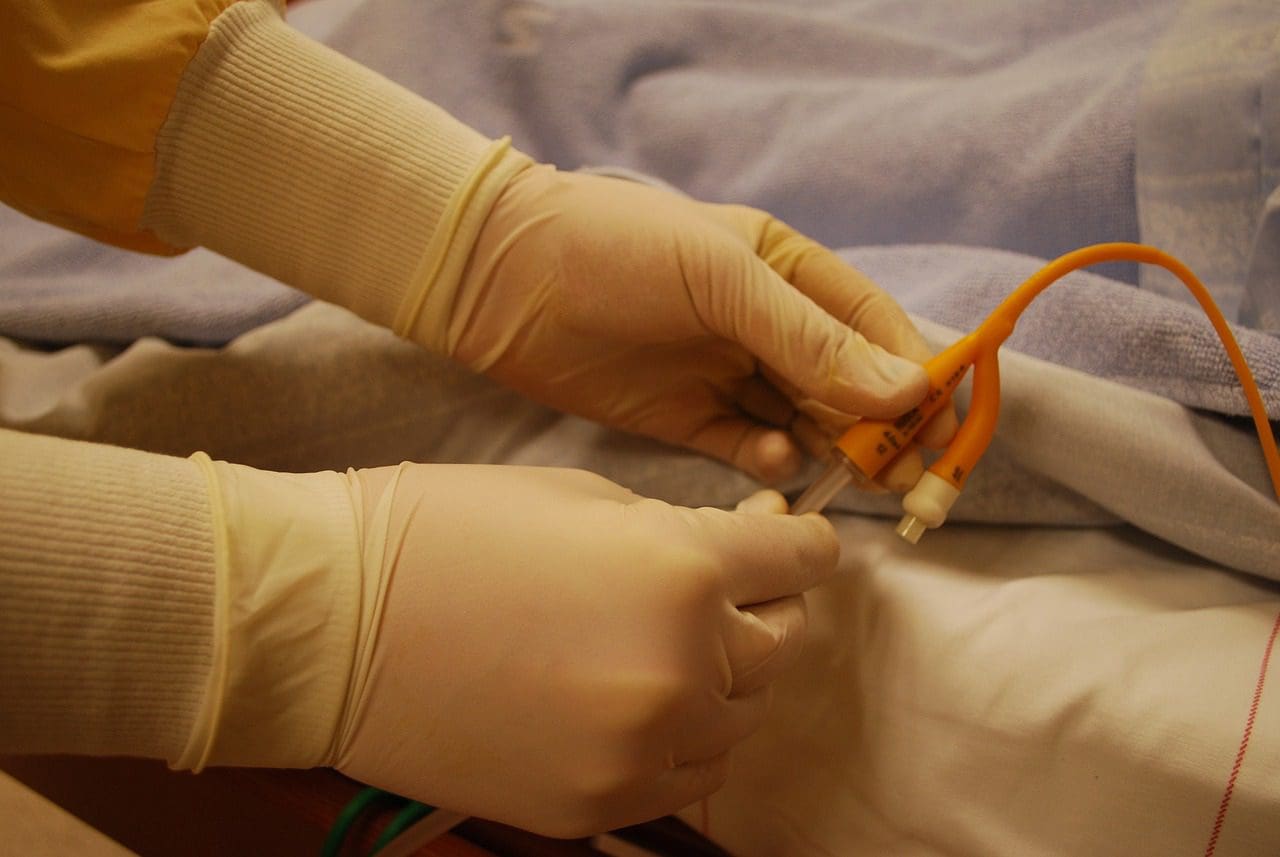
What is Tunneled Catheter?
Tunneled catheters are a subtype of catheters used to administer medicines to patients in whom the power or oral ingestion or multiple needle insertions are not possible.
The veins are almost always chosen to be either in the neck, groin, near the liver or chest. These areas are rich in important blood-carrying veins. The tunneled catheters continue up to the heart.
The insertion of tunneled catheters must be done by an operation, as the removal has to be done via an operation under the medication and supervision of a doctor.
The advantage of a tunneled catheters lies in the direct communication with the heart, but a lot of complications may occur with tunneled catheters, such as infections, blood clots, damage to inserted veins and so on.
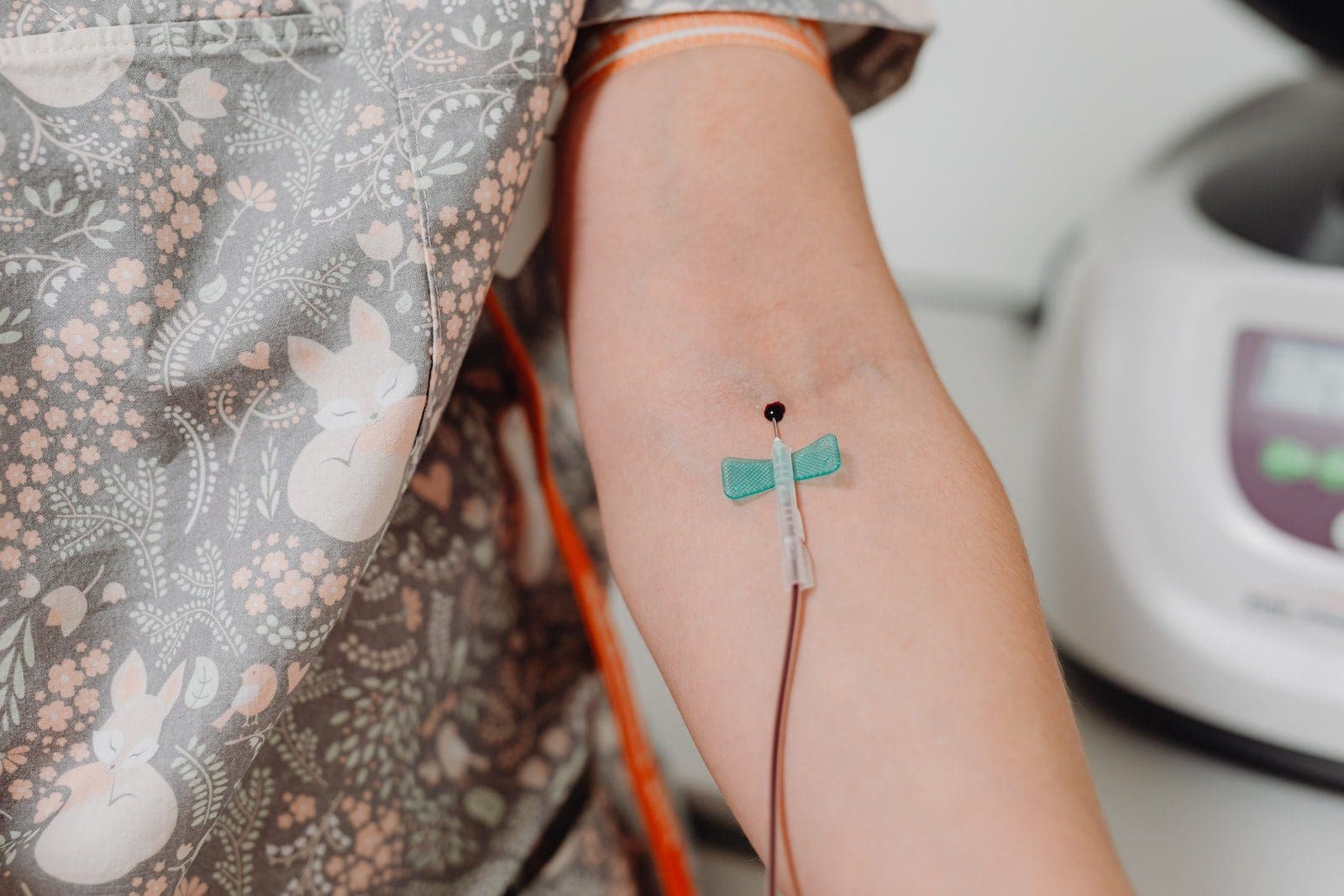
What is Non-Tunneled Catheter?
Non-Tunneled catheters are a subtype of catheters bused to administer medicines to patients in whom the power of oral ingestion of multiple needle insertions is not possible for the time being.
Non-Tunneled catheters are placed for temporary functions and are removed when the need does not persist, or the patient is able to register needle insertions.
Non-tunneled catheters do not have any cuff as well because the catheters, being temporary, do not pose much threat to blood backflow.
The advantage and disadvantages of non-tunneled catheters are similar to a tunneled one, however, it runs a low risk of any kind of infection or complication in comparison to a tunneled catheters.
Main Differences Between Tunneled and Non-Tunneled Catheter
- Chances of infection are high in the case of tunneled catheters in comparison to non-tunneled catheters.
- Tunneled catheters are permanently placed in the body of a patient, while non-tunneled catheters are placed temporarily.
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/pmc3132329/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S154855951200081X

The information is quite valuable. There’s a lot to learn from this.
Agreed. The post is full of useful information.
This post is a bit too long and redundant. Could have been more concise.
I respectfully disagree. The level of detail made this a great read.
I understand what you’re saying, but I think the detail was necessary.
The article provides a lot of valuable information. It’s very useful.
Definitely agree. There’s so much to take away from this post.
Certainly a detailed and insightful piece of writing.
This article is too scientific. Can be difficult for some readers to understand.
Quite a comprehensive guide on catheters. This is helpful.
Very well-written and informative. I enjoyed reading this.
The content is very informative and clear. Loved reading it!
This is a very informative post indeed. Good job!
This article can really help medical professionals understand the differences better.
Absolutely. It’s a great resource.